Thermal printing Fast, flexible, and high-quality identifications – Thermal printing describes a series of printing processes that are based on the punctual application of heat. One of these processes is thermal transfer printing. Phoenix Contact uses this in the THERMOMARK series of printing devices. With the proven thermal transfer technology, the printers are characterized by fast, high-quality, and consistent print results.

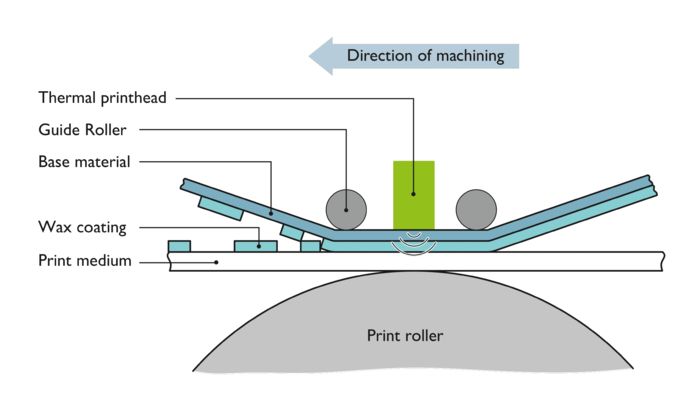
Thermal transfer printing The technology
During the thermal transfer printing process, the desired print image is generated through a spot heat generation of a multi-layer ink ribbon without greater mechanical influence of the marking material (Greek thermós = warm). In the printhead, a heating element (dot) is integrated for each pixel. The heating element can be computer controlled. As the ink ribbon is fed along the printhead in synchronization with the marking material, the heating elements in the printhead are heated according to the desired print image. The heat and contact pressure initiate precise ink transfer to the marking material.
Your advantages
- Reliability and high availability with the proven thermal transfer printing technology
- Precise, consistent, and fast printing of small bar codes, symbols, and Asian characters
- Particularly economical marking of large order volumes
- Very easy servicing with low-maintenance operation

Print resolutions
Printheads The structure of different printhead versions
One of the most important components in a thermal transfer printer is the printhead. It contains a large number of heating elements that can be computer controlled. They melt the color layer on the ink ribbon and then transfer it to the print medium.
A heating element (dot) is integrated in the printhead for each pixel. The number or density of the individual heating elements and the temperature changeover frequency determine the resolution of the print image (dots per inch = dpi). The printhead versions differ with regard to the arrangement of the heating elements.
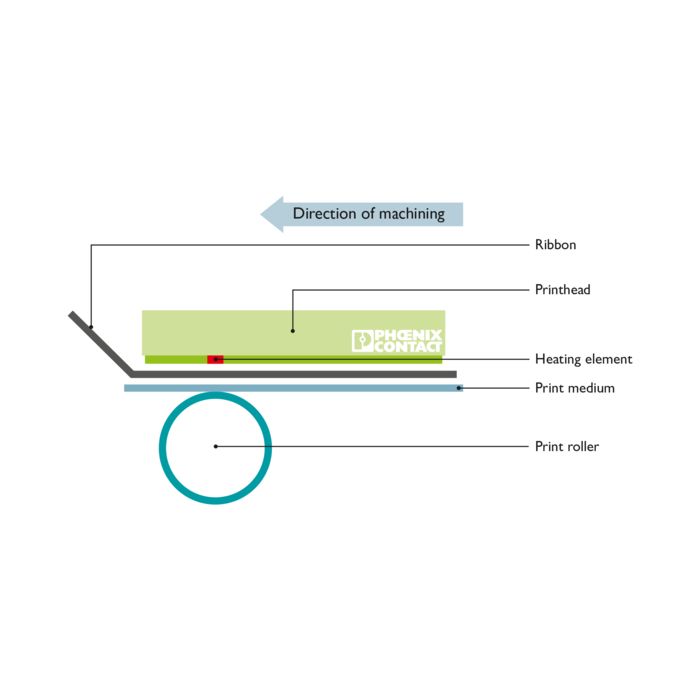
Flathead printhead
The heating elements in flathead printheads are located a few millimeters away from the edge of the carrier plate. The ink ribbon and the print medium run simultaneously for a short time and are slowed and separated out. These printheads are particularly suitable for printing on materials off the roll. Phoenix Contact uses the flathead printhead in the THERMOMARK ROLL 2.0 and in the THERMOMARK E SERIES devices.
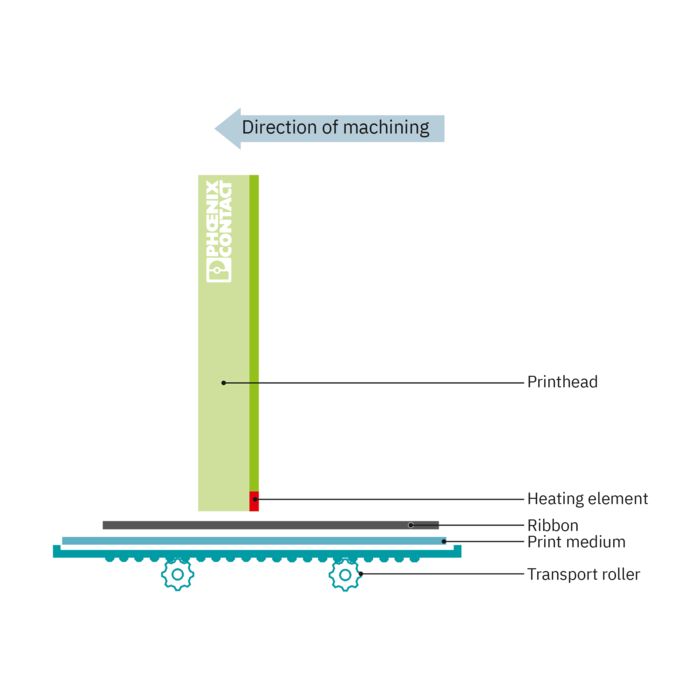
True edge printhead
In true edge printheads, the heating elements are not located on the carrier plate, but on the thin front side. These printheads are height-adjustable and are therefore particularly suitable for printing on hard materials. Phoenix Contact uses this design in the THERMOMARK CARD 2.0 and THERMOMARK PRIME 2.0 products.
Ink ribbons at a glance
Three different types of ribbon are commonly used in the thermal transfer printer process.
| Wax ink ribbons | Resin ribbons | Wax-resin-mixed ribbons | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ribbon type | |||
| Properties of the print image | Sharp and easy to read, even on rough surfaces | Heat-resistant, smudge-resistant, scratch-resistant, very durable, and resistant to solvents and chemicals | Heat-resistant, smudge-resistant, and scratch-resistant, resistant to solvents and chemicals |
| Materials to be marked | Paper | Films and plastic surfaces | Paper and plastic |
| Technical requirements | Low printing energy | High printing energy, low printing speed | Medium printing energy, high printing speed |
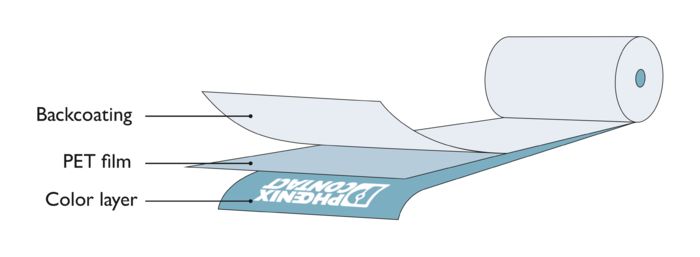
Our ink ribbons
Phoenix Contact uses resin ribbons and wax-resin mixed ribbons. These consist of four layers:
- Back coating: this protects the PET film and the printhead, reduces static electricity, and improves the flow of the ink ribbon in the printhead.
- PET film: this ensures good heat transfer from the printhead to the ink.
- Release layer: this supports a clean transfer of the ink even at low temperatures.
- Color layer (ink): during printing, this melts and is transferred to the substrate.