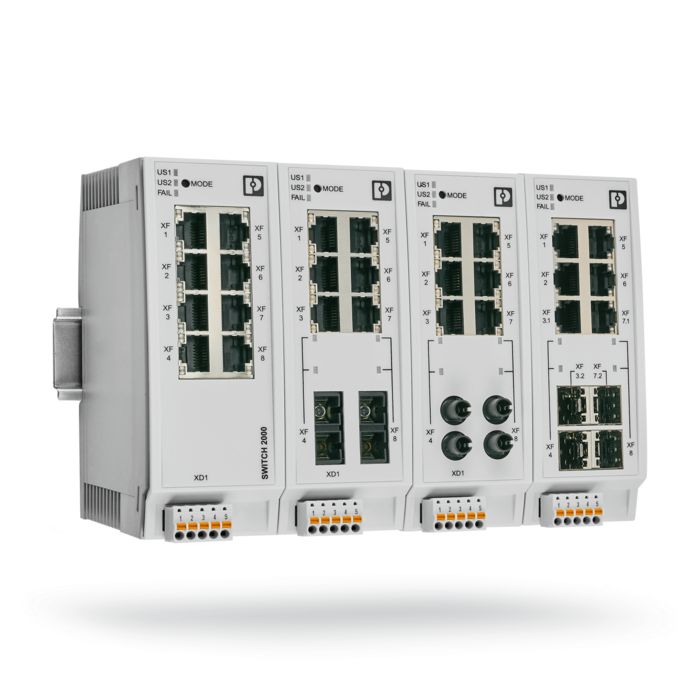
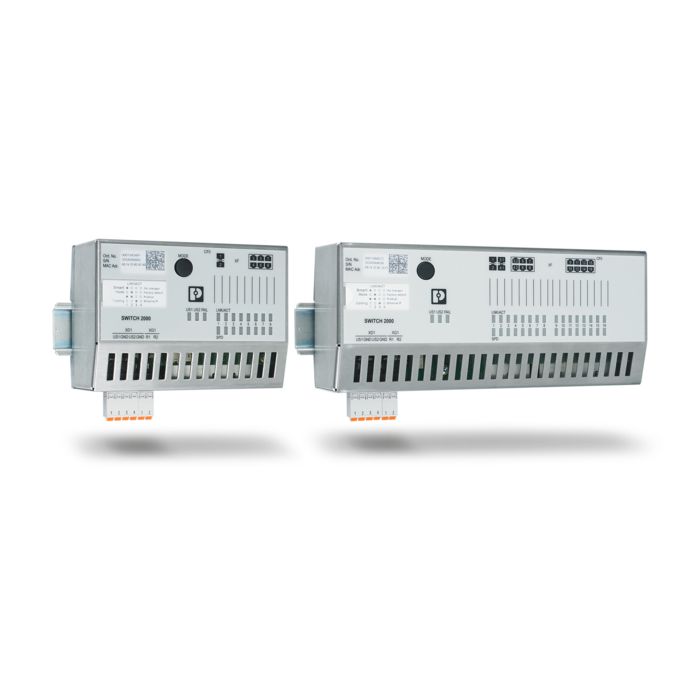
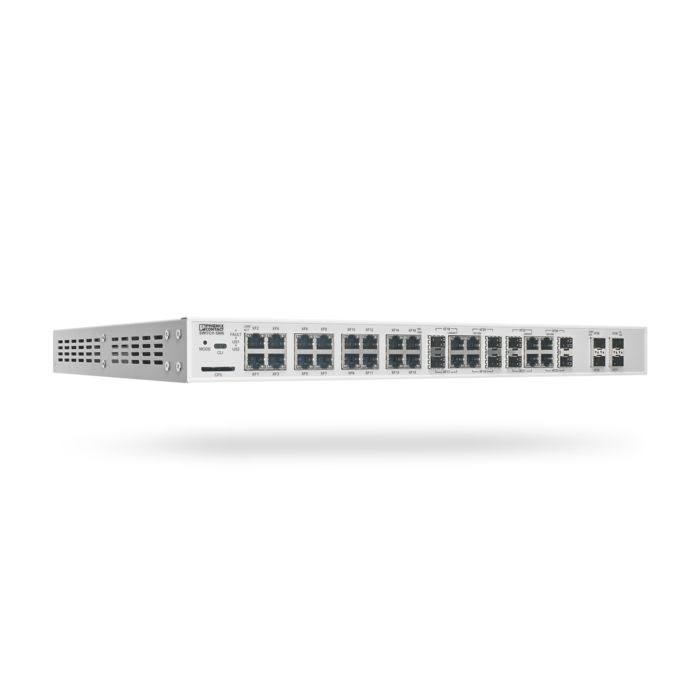
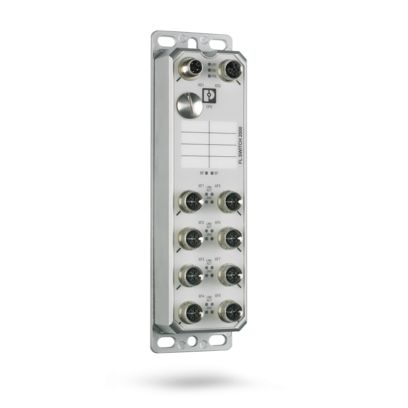
| Transmission speed |
10/100 Mbps (FL SWITCH 2000), 10/100/1000 Mbps (FL SWITCH 2100) |
10/100 Mbps (FL SWITCH 2200), 10/100/1000 Mbps (FL SWITCH 2300) |
10/100 Mbps (FL SWITCH 2400), 10/100/1000 Mbps (FL SWITCH 2500) |
10/100/1000 Mbps, 10 Gbps |
| Jumbo frames |
only with the 2100 versions |
only with FL SWITCH 2300 versions |
only with FL SWITCH 2500 versions |
yes |
| Alarm contact |
– |
yes (digital output) |
yes (relay contact) |
– |
| Temperature range |
0°C … +60°C |
-40°C … +70°C |
-40°C … +70°C |
-10°C … +60°C |
| Supply voltage |
18 V DC … 32 V DC |
12 V DC … 57 V DC (redundant) |
18 V DC … 32 V DC (redundant) |
100 V AC … 240 V AC |
| Filter functions |
Quality of Service, VLAN, Multicast / IGMP Snooping |
Quality of Service, VLAN, Multicast / IGMP Snooping |
Quality of Service, VLAN, Multicast / IGMP Snooping |
Quality of Service, VLAN, Multicast / IGMP Snooping |
| Redundancy |
RSTP, MRP client |
RSTP, MRP manager/client, FRD, LACP, Large Tree Support |
RSTP, MRP manager/client, FRD, LACP, Large Tree Support |
RSTP, MRP manager/client, FRD, LACP, Large Tree Support |
| Management functions |
Port configuration, ACD, port-based DHCP server, CLI |
Port configuration, ACD, DHCP server (pool/port-based, option 82), CLI |
Port configuration, ACD, DHCP server (pool/port-based, option 82), CLI |
Port configuration, ACD, DHCP server (pool/port-based, option 82), CLI |
| Diagnostic functions |
Port statistics and utilization, LLDP, SNMPv1/v2/v3, SNMP traps, syslog |
Port statistics and utilization, LLDP, SNMPv1/v2/v3, SNMP traps, syslog |
Port statistics and utilization, LLDP, SNMPv1/v2/v3, SNMP traps, syslog |
Port statistics and utilization, LLDP, SNMPv1/v2/v3, SNMP traps, syslog |
| Time synchronization |
– |
Simple Network Time Protocol (SNTP) |
Simple Network Time Protocol (SNTP) |
Simple Network Time Protocol (SNTP) |
| Cybersecurity – network access |
RADIUS authentication (IEEE 802.1X) |
MAC-based port security, RADIUS authentication (IEEE 802.1X) |
MAC-based port security, RADIUS authentication (IEEE 802.1X) |
MAC-based port security, RADIUS authentication (IEEE 802.1X) |
| Automation protocols |
PROFINET Conformance Class A, EtherNet/IP™, Extend multicast filtering |
PROFINET Conformance Class B, PROFINET device, EtherNet/IP™, Extend multicast filtering |
PROFINET Conformance Class B, PROFINET device, EtherNet/IP™, Extend multicast filtering |
PROFINET Conformance Class B, PROFINET device, EtherNet/IP™, Extend multicast filtering |
| Approvals |
– |
Maritime approvals, ATEX, IECEx |
Maritime approvals |
– |