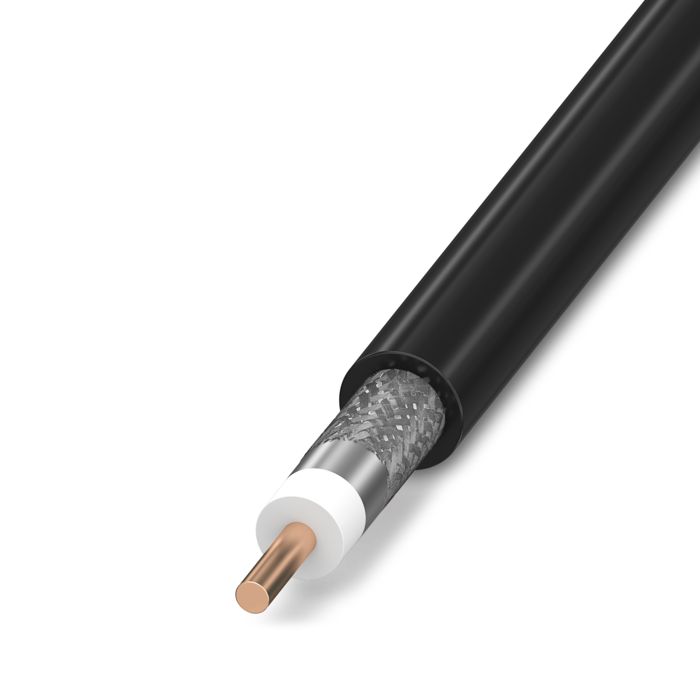
The cable sheath on coaxial cables protects the internal elements of the cable from external influences. In order to improve mechanical or thermal properties and resistance levels, this sheath is usually made from plastic materials mixed with additives. For example, it is thus possible to make cables suitable for outdoor use and to achieve resistance to moisture and sunlight.
The inner conductor can be solid or made up of thin wires. In both cases, the cable is referred to as a flexible cable.
Many flexible coaxial cables feature shielding with tightly braided metal litz wires. To achieve better shielding properties, a metal or metal-coated plastic foil can also be used in addition. In contrast, there are cables with a solid outer conductor. These rigid cables are called semirigid cables.
The dielectric is the insulation material between the inner and outer conductors. This can consist of solid plastic, as well as plastic discs or, as in most cases, a plastic foam, e.g., polyethylene.