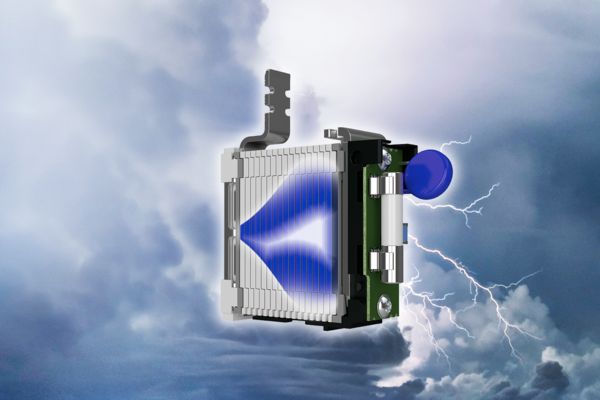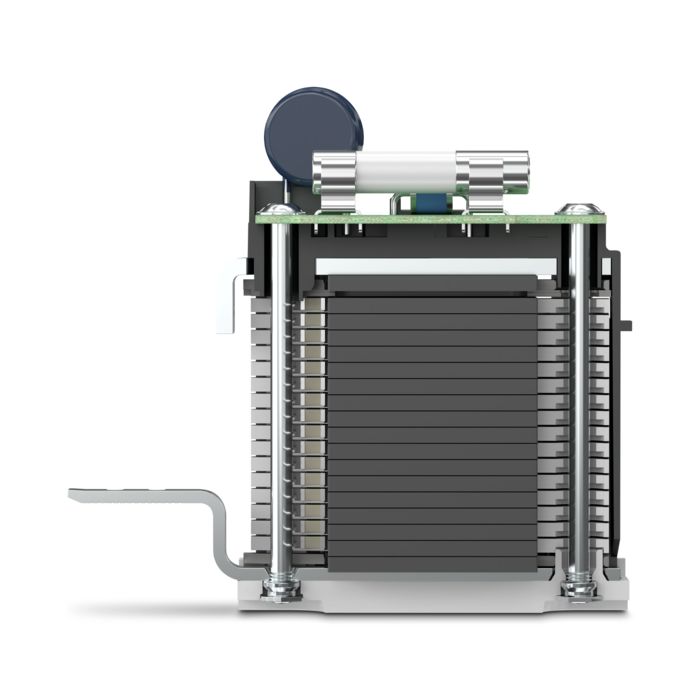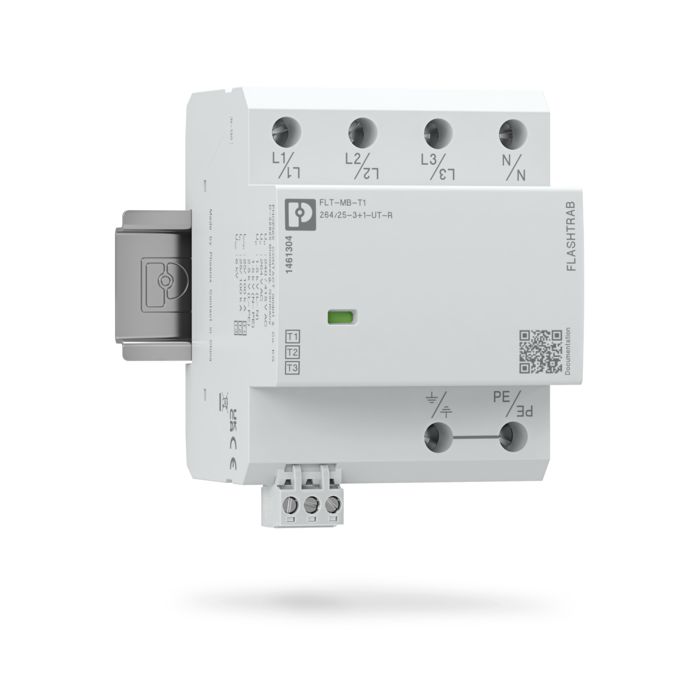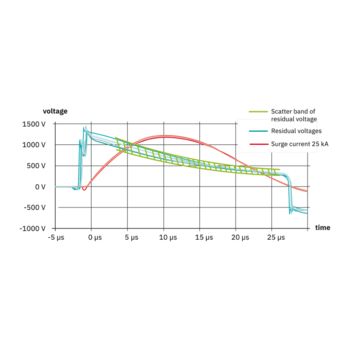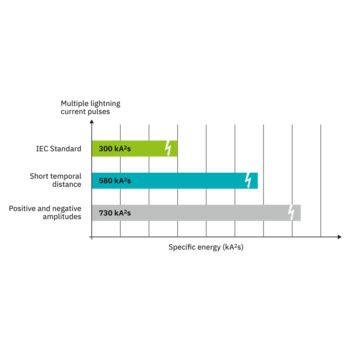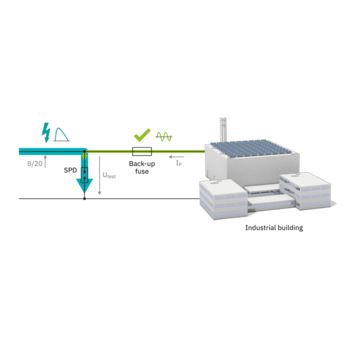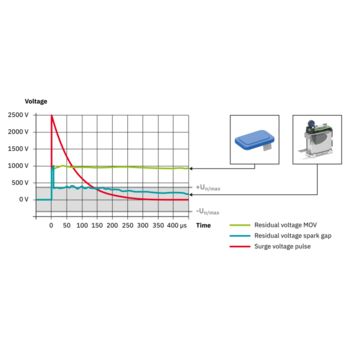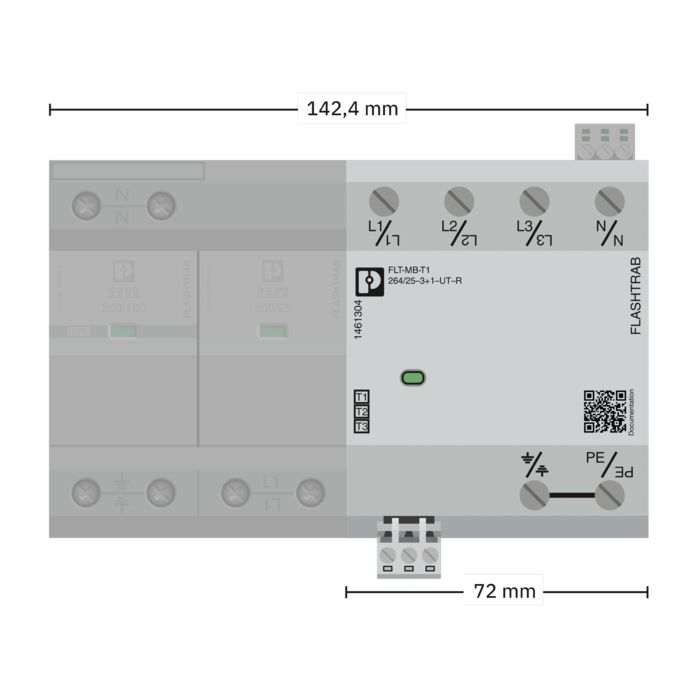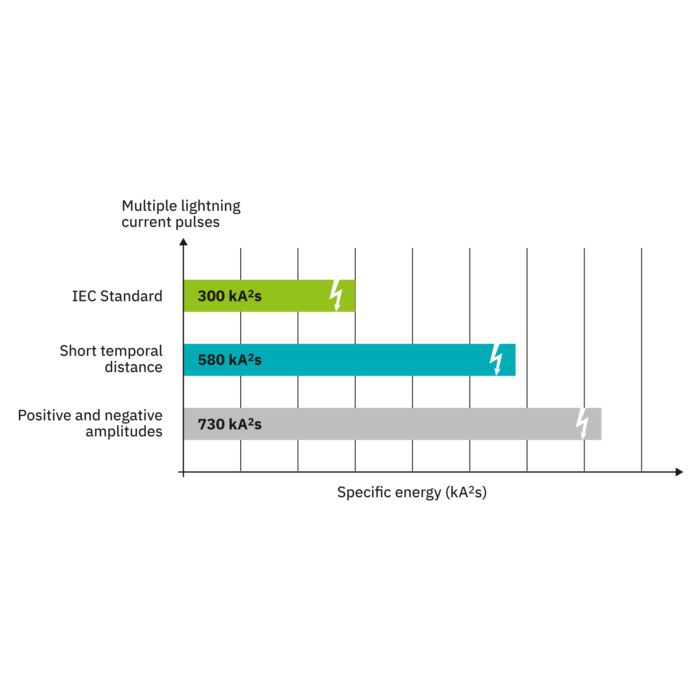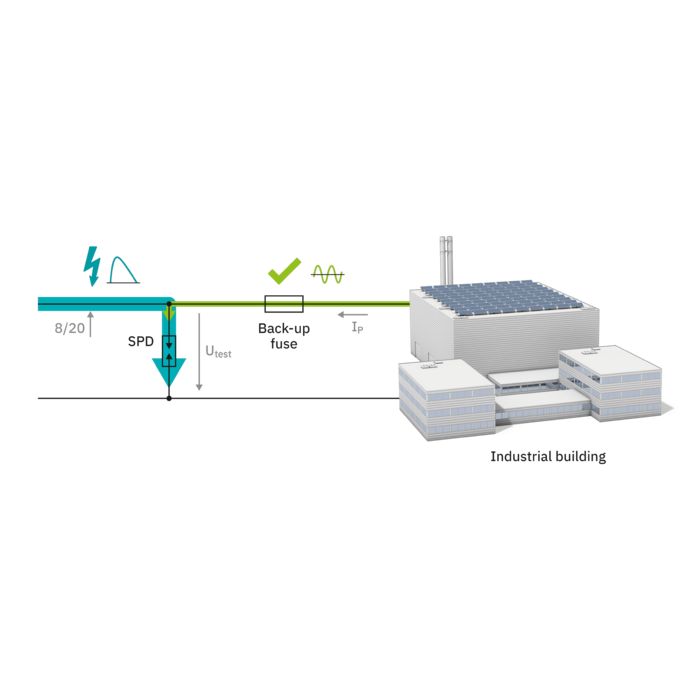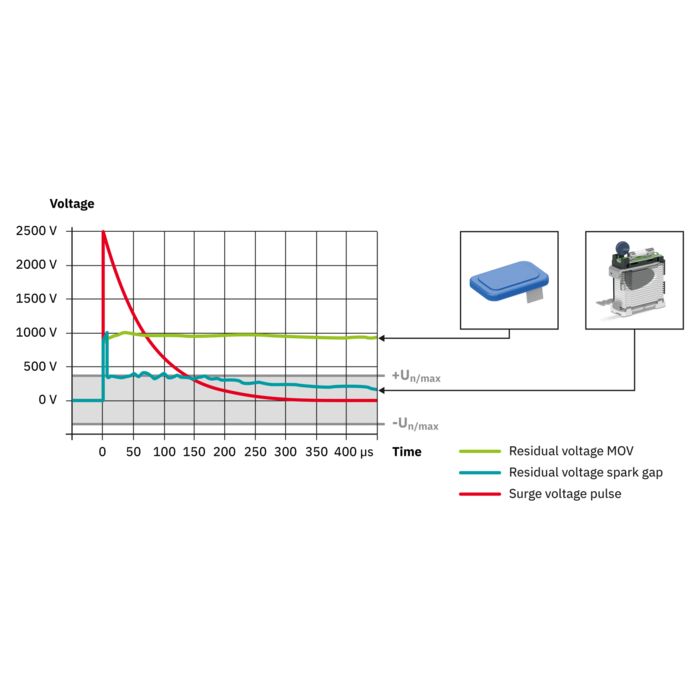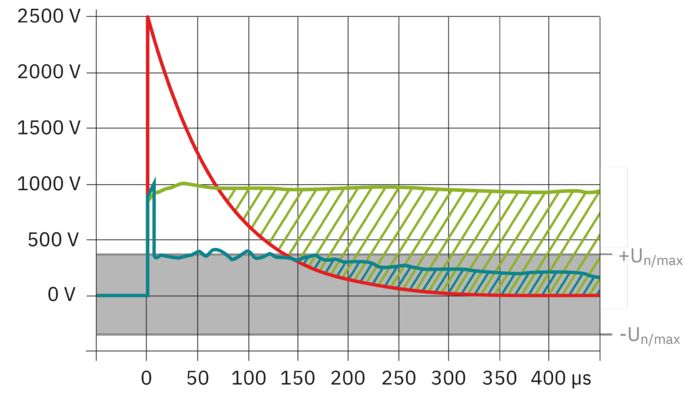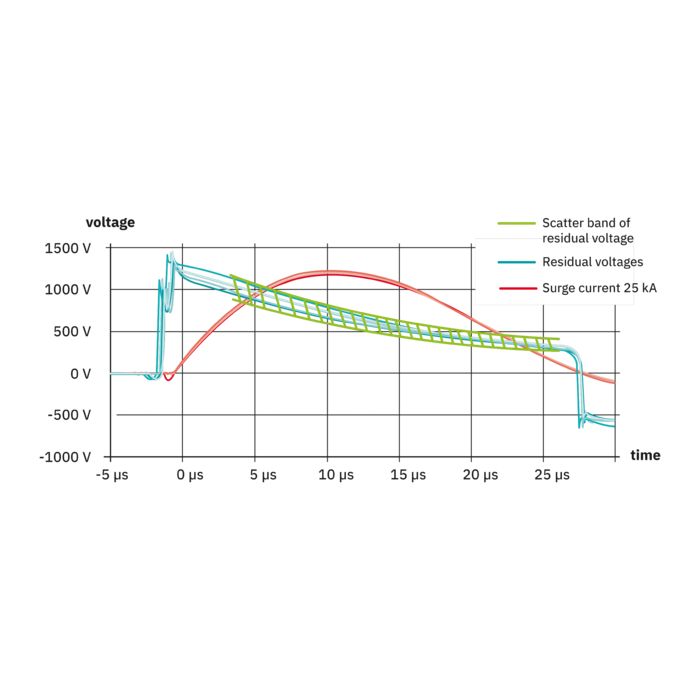
The new multi-carbon spark gap uses particularly robust materials. The energy to be dissipated is distributed ideally over the entire installation space. As a result, it shows no signs of aging, even after multiple loads that exceed the normative requirements.