Energy automation
Use the products from the COMPLETE line system to protect, control, and test the devices in your energy applications. Realize a wide range of solutions, tailored to the demands of various applications and the surrounding conditions.
Building solutions for energy automation
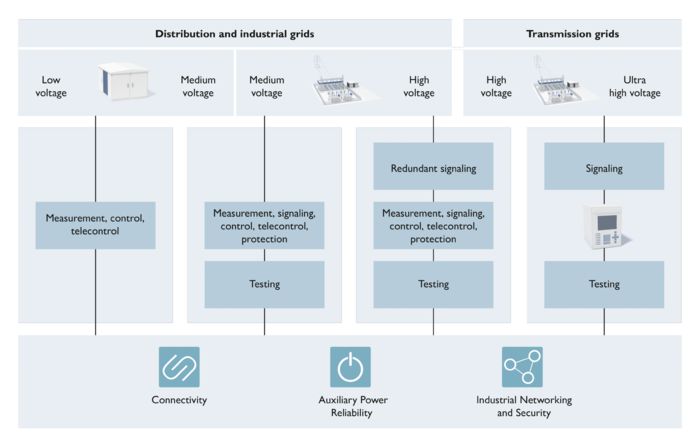
Distribution grids and industrial grids for low and medium voltage
The structure of distribution grids differs greatly depending on regional and national conditions. In urban areas, secondary substations are often the connection point between medium and low-voltage grids. Normally, they include a compact medium-voltage switchgear system, a secondary grid transformer, and a low-voltage distribution system. In rural areas, electricity is often supplied via transmission line grids due to the great distances involved. Here, secondary substations are often designed as open-air systems, also known as mast stations. Due to the ongoing expansion of renewable power generation and the planned development of a charging infrastructure for e-mobility, the need for monitoring the status of the grid via intelligent measurement and remote control technology is growing.
Distribution grids and industrial grids for medium and high voltage
Electricity is distributed at the regional level in the medium to high-voltage range. Substations are the nodes of these grids. In the medium-voltage switchgear systems installed in these substations, special protective relays handle the mains protection. These devices combine many tasks: Along with various protective functions, they also feature measurement, signaling, control, and remote monitoring functions. National standards and directives stipulate regular testing of the protective relays in medium-voltage applications. The easily accessible test interfaces ensure that the necessary repeat testing can be carried out safely.
Devices that will be used in high-voltage switchgear systems satisfy even higher demands on availability and safety. Therefore, protective relays for these systems are often designed to be redundant. The number of connection test points increases with the number of measuring systems and protective relays. As a result, the effort involved in connecting the test device increases, as does the risk of incorrect connections. Standardized test interfaces counteract this risk. Moreover, in high-voltage applications, a redundant signaling system often combines the most important alarms and messages so that even if a device suffers a failure, important messages are not lost.
Transmission grids for high and ultra-high voltage
This voltage level has the highest complexity and therefore the highest requirements in terms of availability. Only special protective relay combinations that are usually distributed across several devices can satisfy this demand to achieve a maximum system availability. Because the number of connection test points is even higher in comparison with medium to high voltage, the effort involved in connecting the test device increases again, as does the risk of incorrect connections. Tailored test interfaces help to minimize this risk. In addition, the size and complexity of these substations means that additional signals are also required. A larger signaling system combines these together and thus features more possibilities for redundant signaling.







