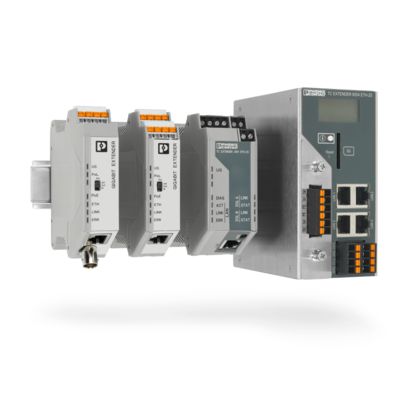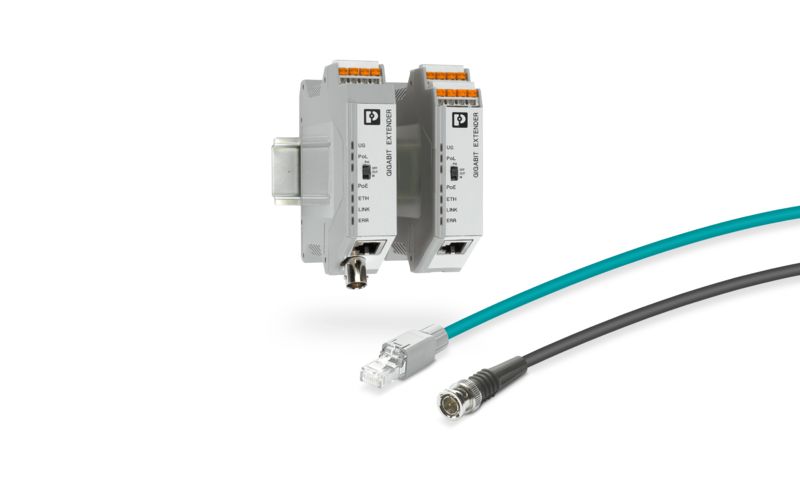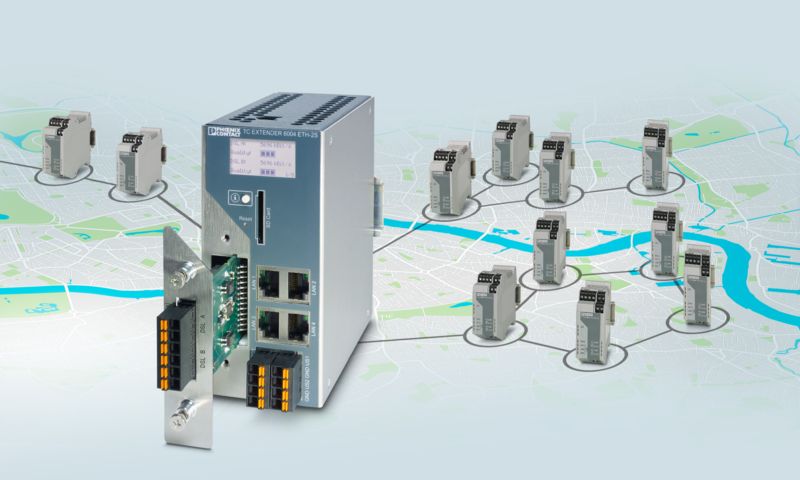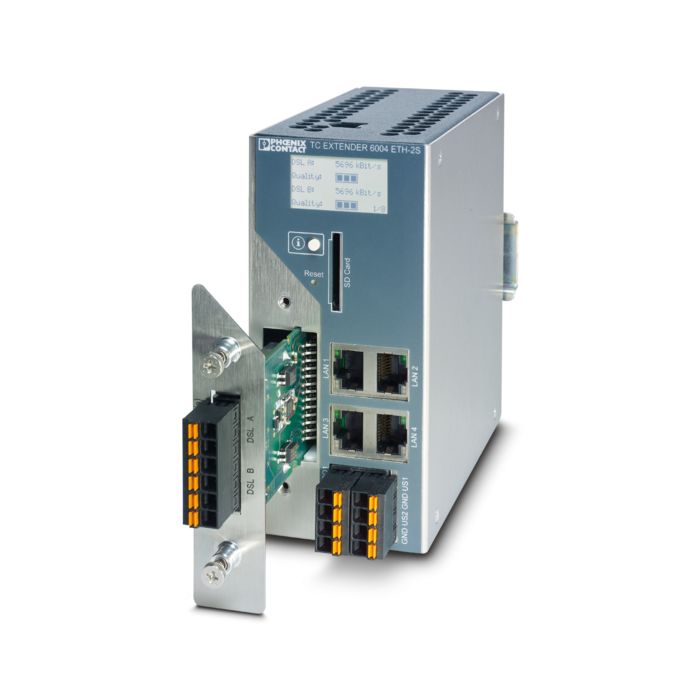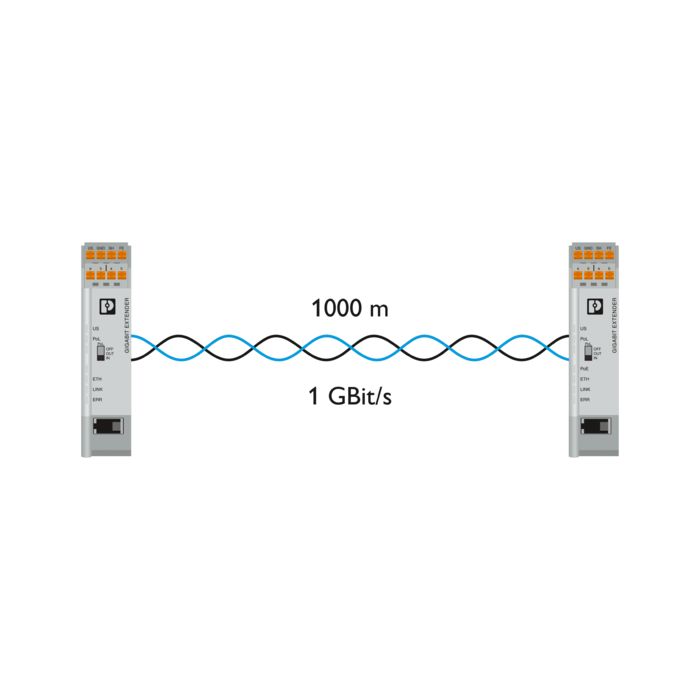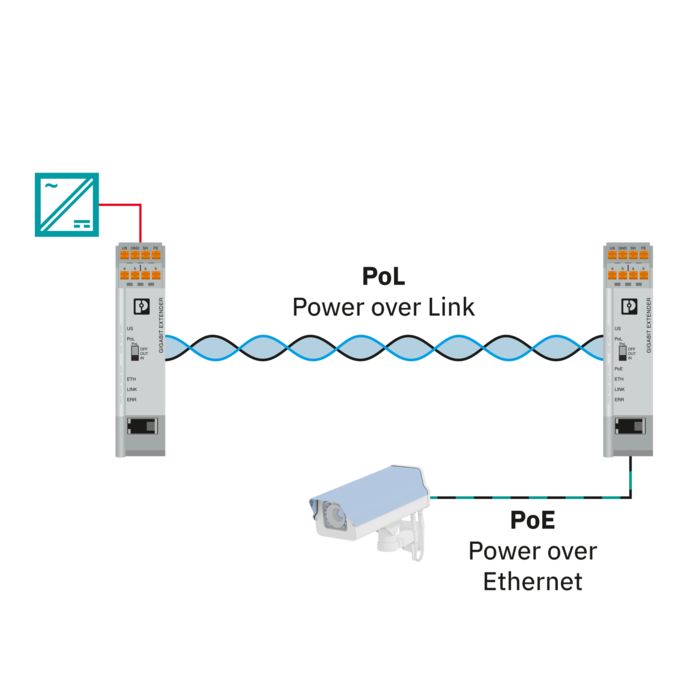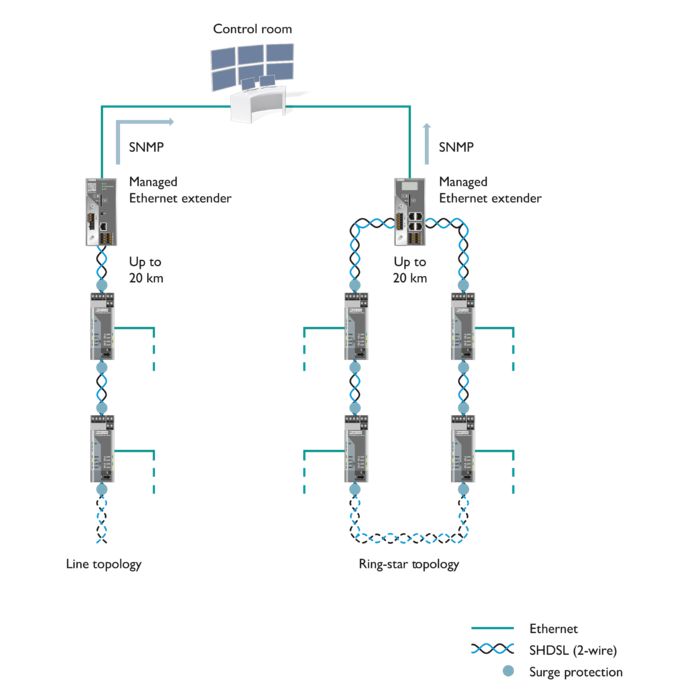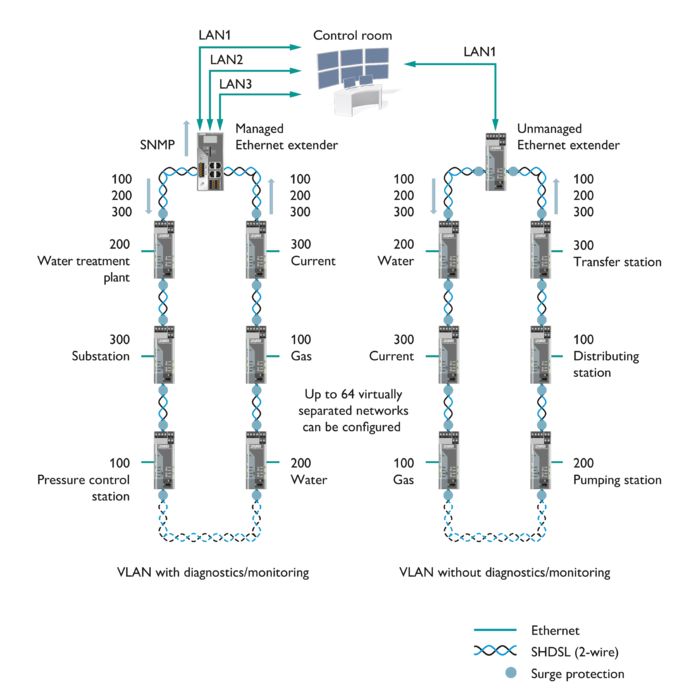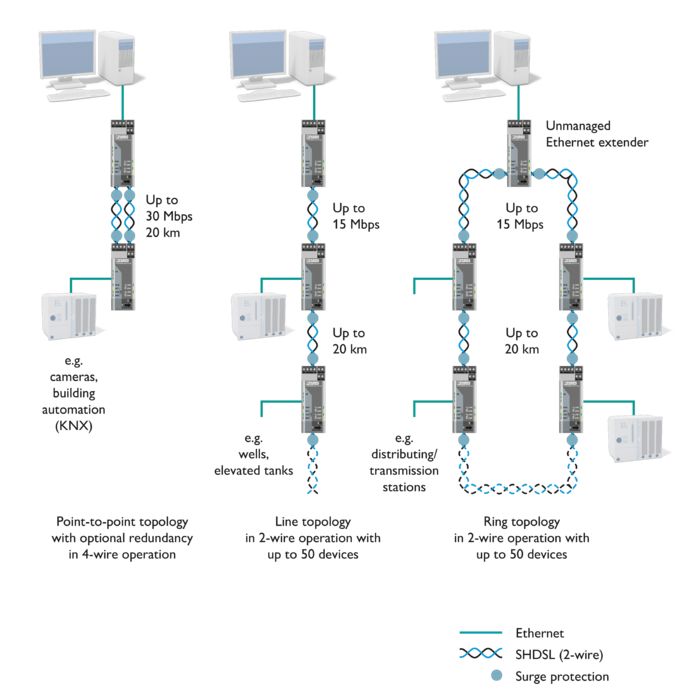
Existing two-wire cables can be used for networking. The system can be extended during operation without causing any adverse impact.
Basic features for quick commissioning via plug-and-play:
• No configuration work necessary
• Time savings with automatic topology and data rate recognition
• Flexible use in point-to-point, line, and ring topologies