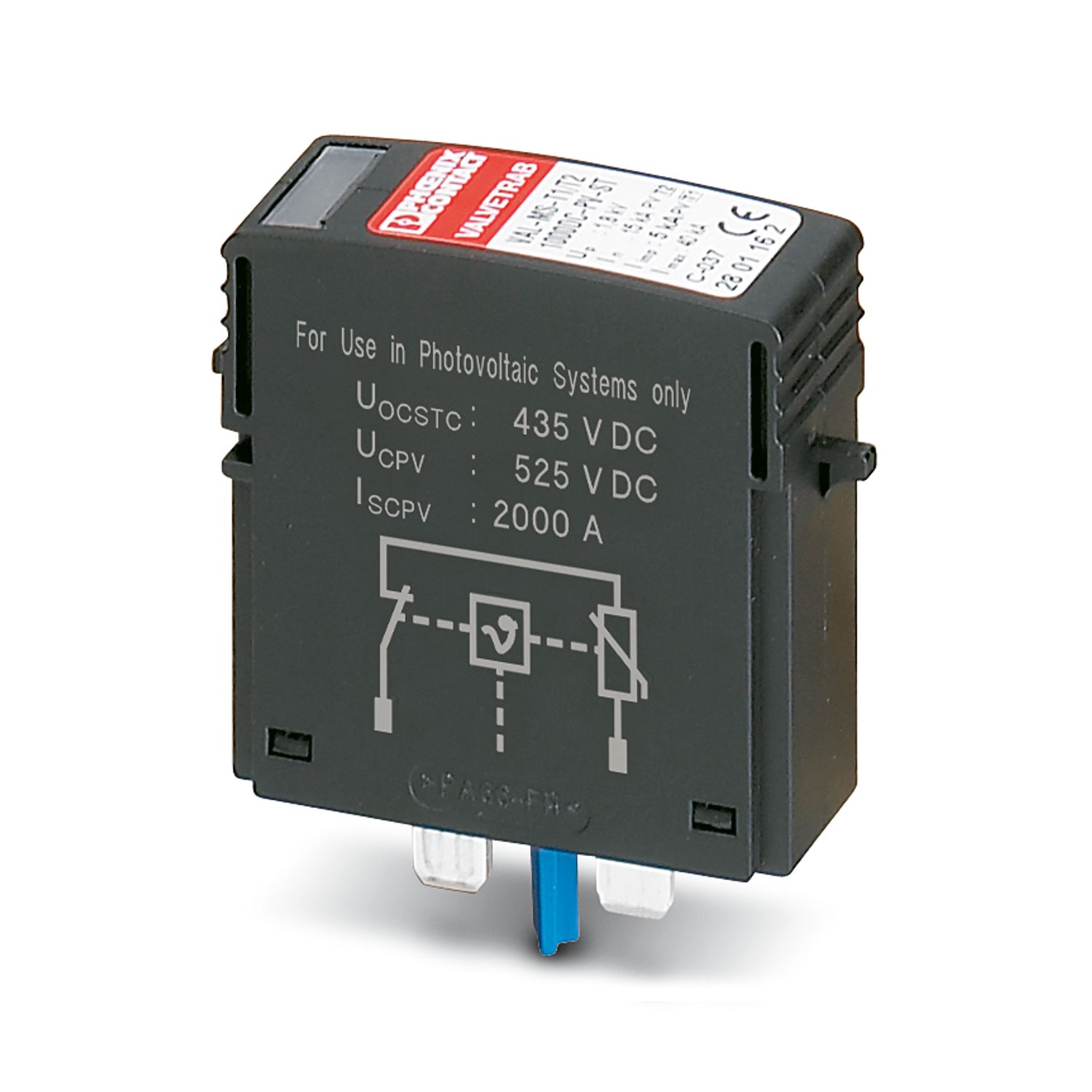
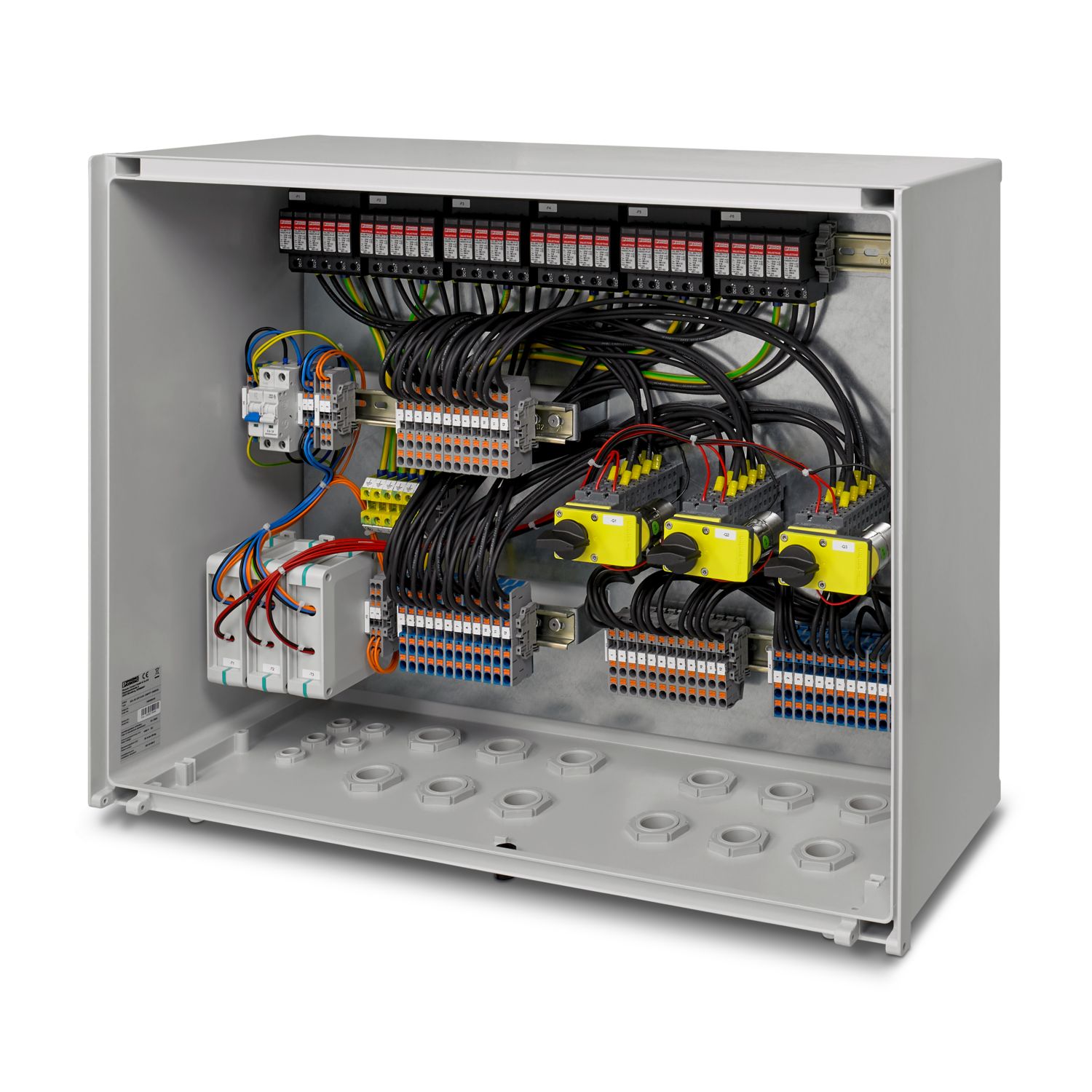
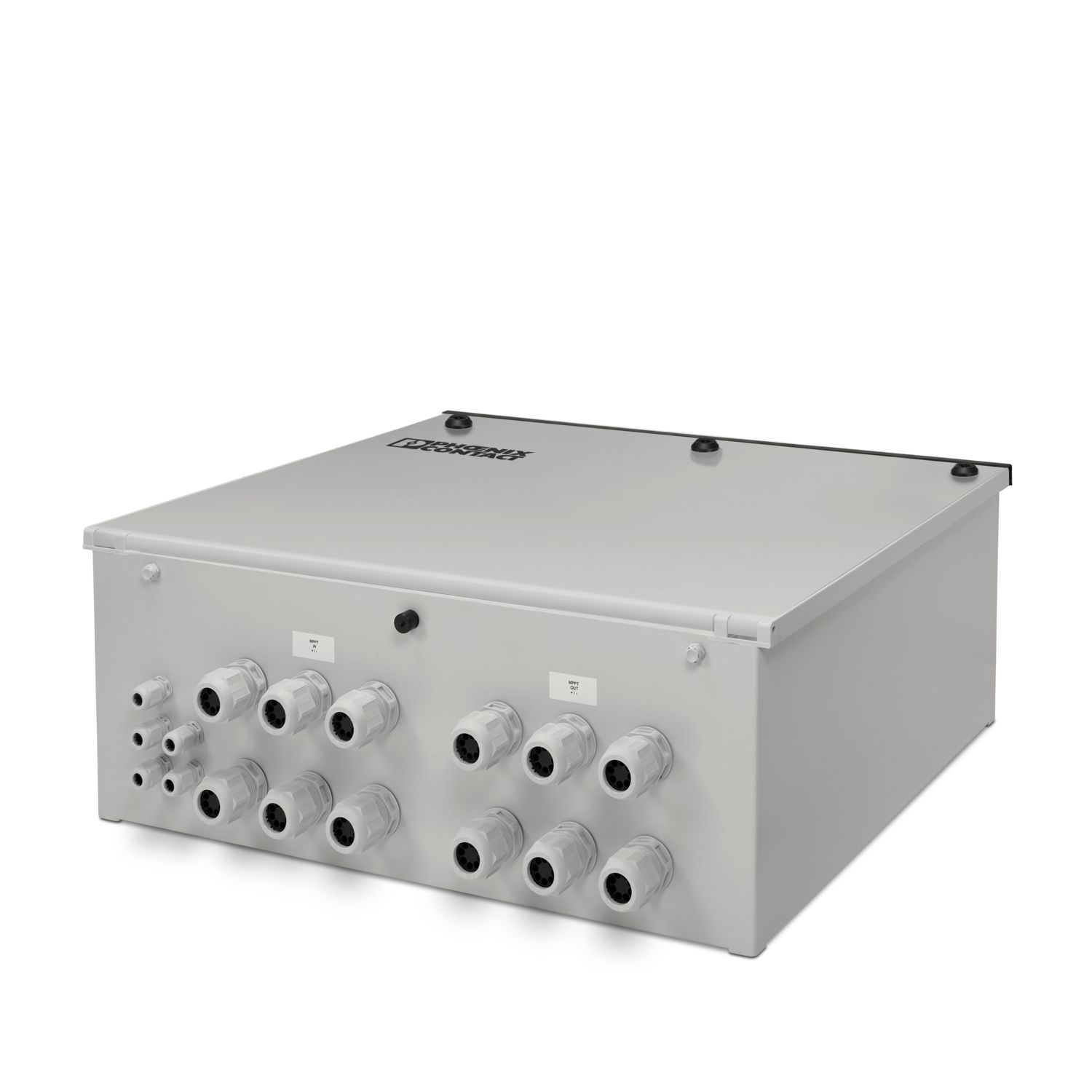
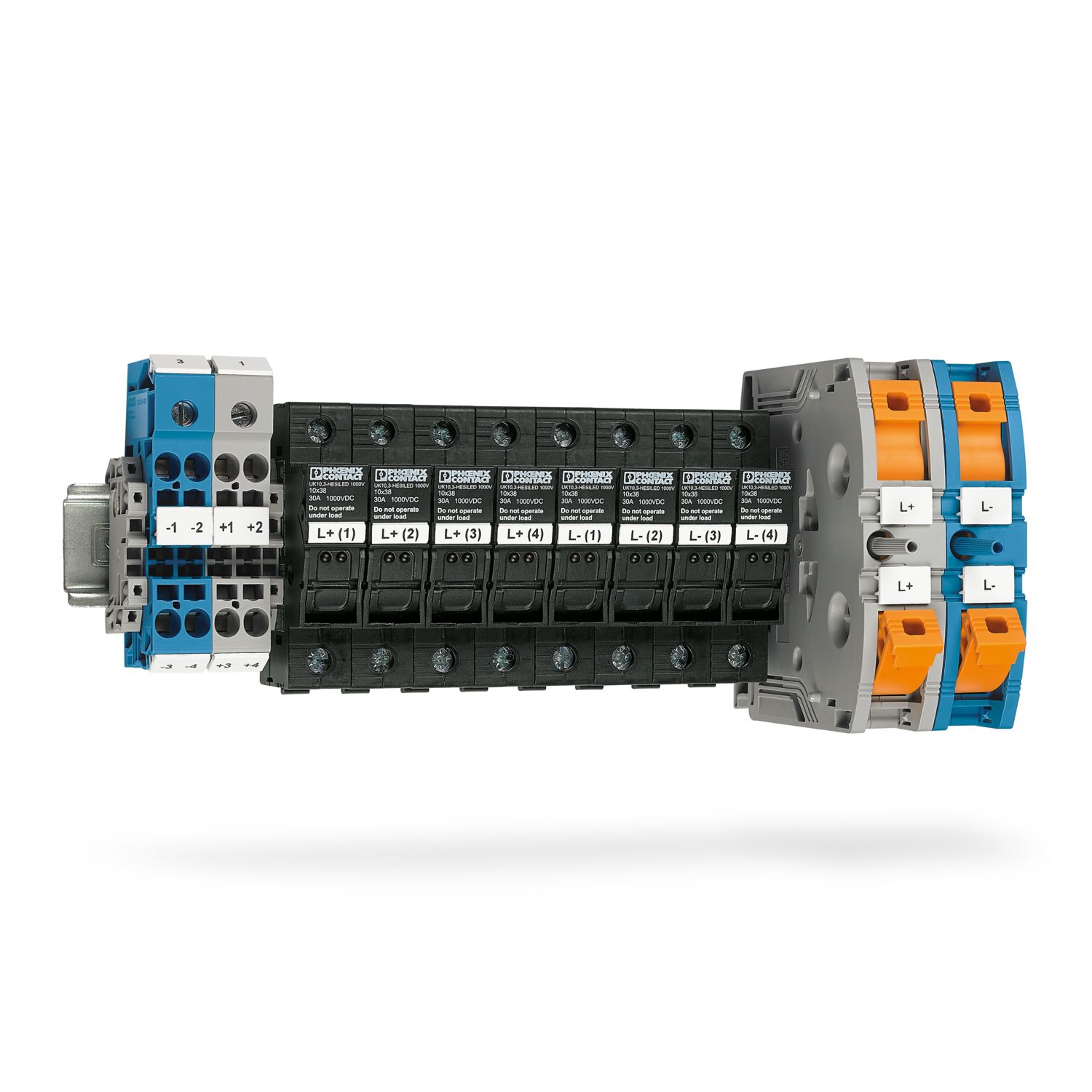
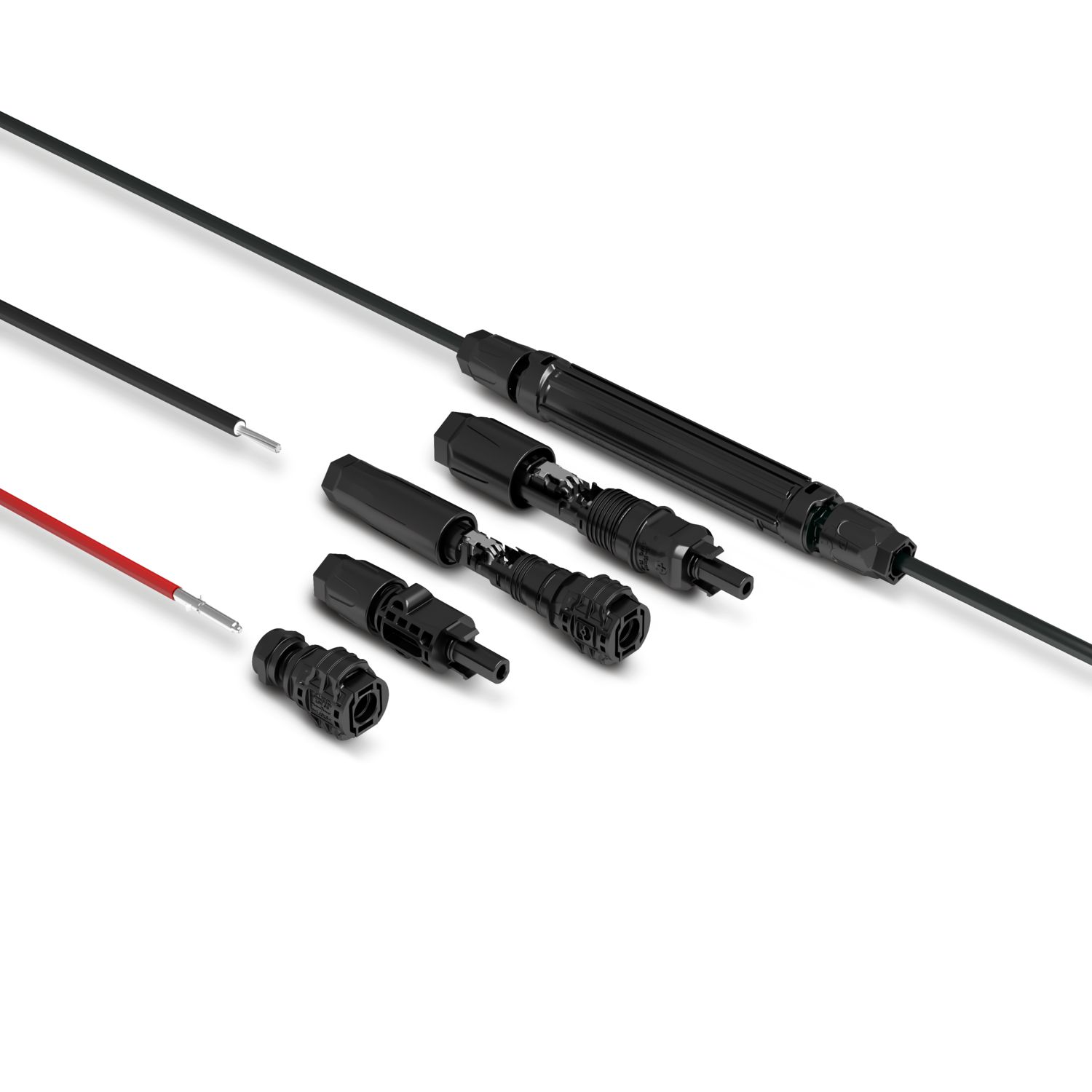
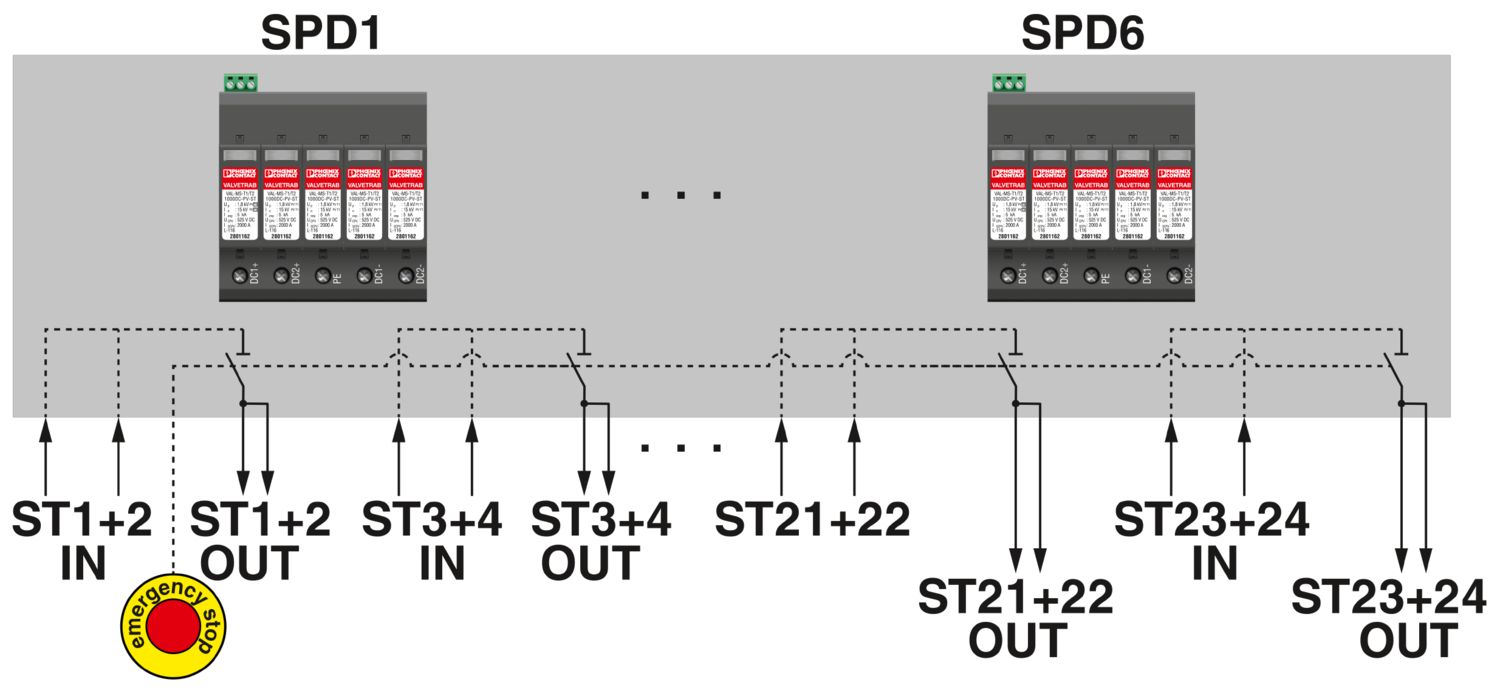
The Solarline string combiner boxes (SCBs) are used in both small rooftop systems and large ground-mounted systems. The main tasks of the SCBs are the surge protection of the photovoltaic system, collecting strings (if necessary), and looping through the protective equipotential bonding conductor for the local equipotential bonding.
Further functions are optional and depend on the equipment.
Examples of optional functions include protecting the strings with string fuses and disconnecting the strings via DC switch disconnectors or DC fire department switches.
You can determine the full scope of functions of the SCB from its item designation (see the application note for the type key of the SCB, which can be downloaded in the “Downloads” area).