
From product development to the production series, the highest Phoenix Contact quality is secured by consistent testing in accordance with uniform guidelines and in-house standards.
Mechanical tests
- Flexion test and torque bending test
- Detent of electrical contacts
- Insertion and withdrawal
- Bending test
- Insertion/withdrawal cycles
- Shock protection
- Polarization/coding
- Shock test
- Polished sections
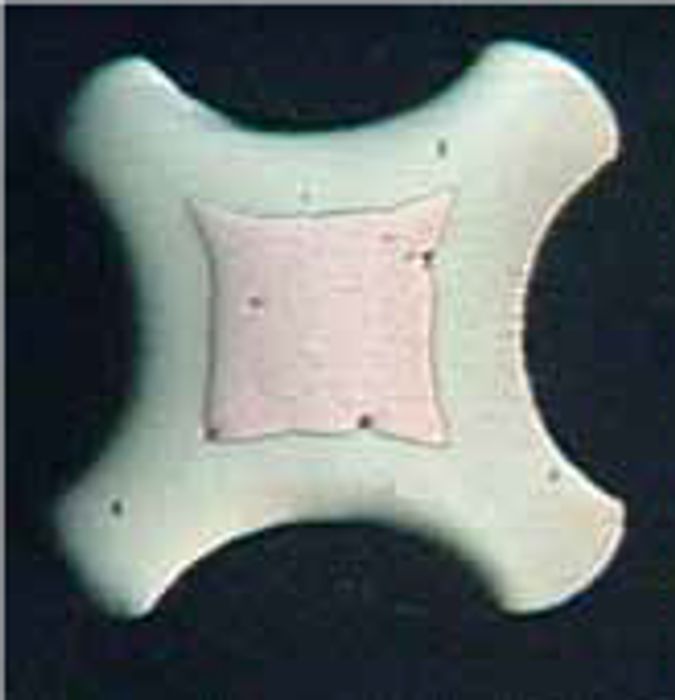
Embedding
- IEC 60352-2
- The quality features of crimping connections are inspected via embedding. This guarantees a reliable electrical connection over the entire life cycle of a cordset.

Torque test
- IEC 60999-1
- Comprehensive mechanical tests are performed to check loads that occur during connection and operation of electrotechnical products.

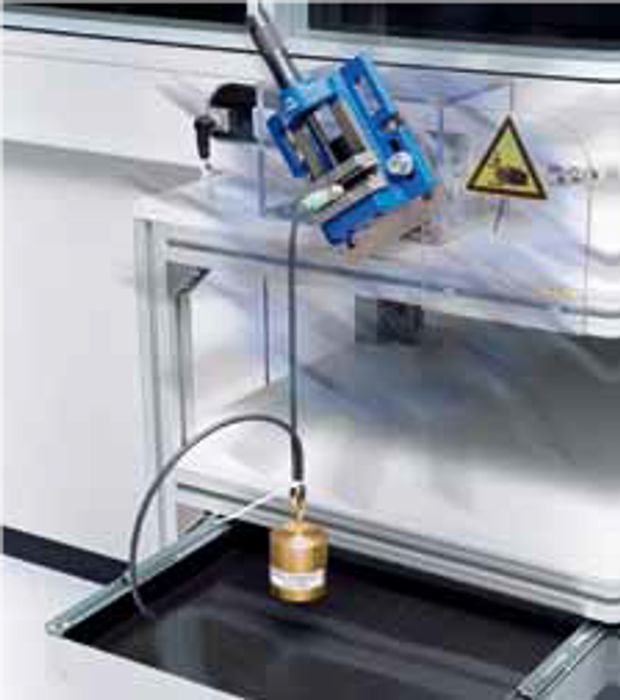
Pull-out force
- IEC 60352-2
- The movable head of the tensile test machine must apply a pulling force to the test object at a rate between 25 mm/min and 50 mm/min until the is cable either pulled out of the crimp sleeve or the wire is torn out of the test object.

Flexion test/twist test
- UL 2238
- Test according to the standard UL 2238 “Cable Assemblies and Fittings for Industrial Control and Signal Distribution”. The cable sample for the Jacket Retention Test is prepared with a 50 mm longitudinal cut in the jacket. The minimum distance from the cut to the connector is 152 mm. All single strands, as well as all inner components (shield etc.) have to be cut. The prepared cable sample is passed through a drilling hole of a diameter adapted to the diameter of the cable. The drilling hole is in a horizontally mounted plate and fixes the sample for the test. A tensile force of 67 N is applied to the lower end of the cable for 2 minutes. Secondly, a weight of 13.7 N is rotated 360° about the horizontal axis of the cable exit.

Strain relief
- UL 2238
- Test according to the standard UL 2238 “Cable Assemblies and Fittings for Industrial Control and Signal Distribution”. The cable of the cordset, which is subject to the Strain Relief Test, is passed through a drilling hole of a diameter adapted to the diameter of the cable. The drilling hole is in a horizontally mounted plate and fixes the sample for the test. A specified weight is applied to the lower end of the cable. During a testing time of 1 minute the cable has to withstand the tensile load and the cable may not slip out of the cordset‘s overmolded head.
Electrical tests
- Cyclic overload test (heat cycling test according to UL 1059)
- Cyclic aging test
- Thermostability
- Insulation resistance
- Contact resistance
- High voltage test
- Surge voltage test
- Air and creepage distances
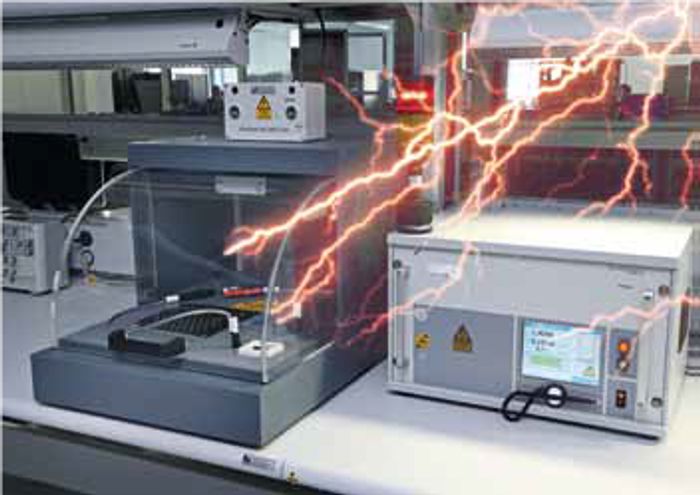

High voltage test
- IEC 60512-4-1
- During this test, each contact is tested against each neighboring contact or potential by applying a defined test voltage. The measuring and test procedure for the connectors for electronic installations is in accordance with IEC 60512-4-1.
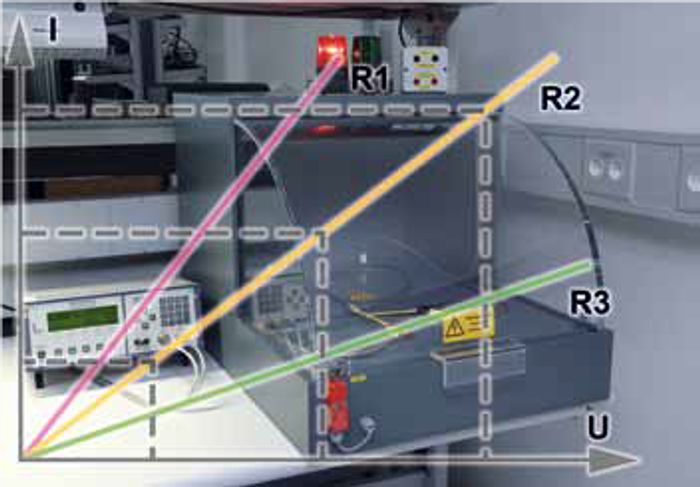
Insulation resistance
- IEC 60512-3-1
- During this test, every contact is tested against every neighboring contact or potential according to procedure A in IEC 60512-3-1. The Insulation Resistance Test consists of measuring the insulation resistance of a device under test, where the measured resistance has to be higher than the indicated limit from the international standards.
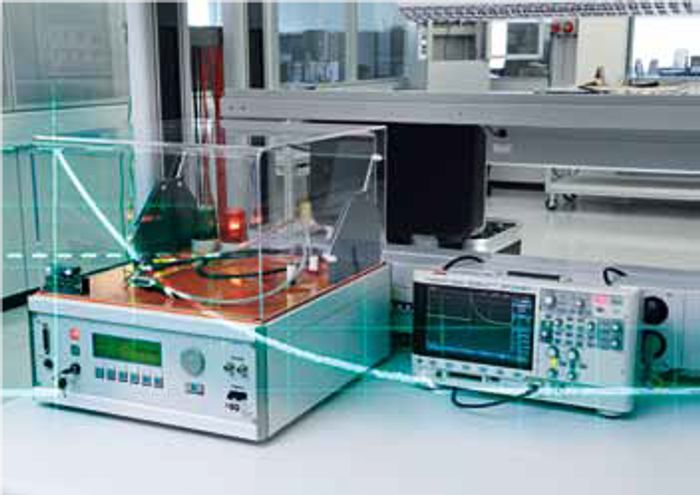

Impulse withstand voltage test
- IEC 60664-1
- Verification of adequately large air and creepage distances between the two adjacent potentials is provided by the impulse withstand voltage test.
- The amount of the test voltage depends on the rated surge voltage of the component. Flashovers may not occur during three power surges (1.2/50 μs) per polarity. The reliable use of the components is confirmed by this test.
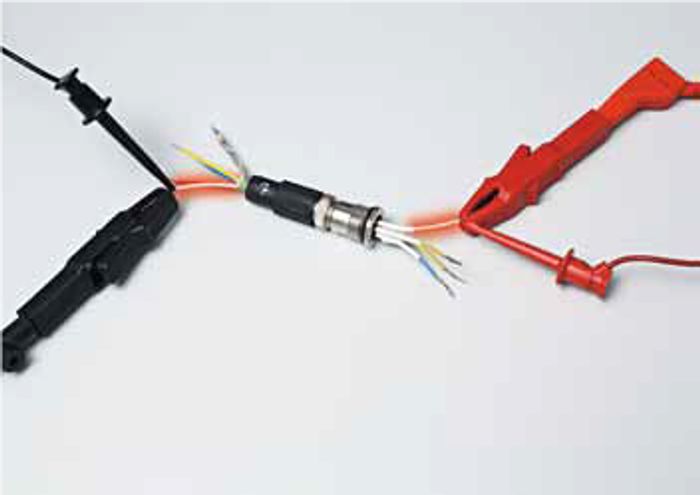

IEC 60512-2-1
- The contact resistance is measured by applying the Millivolt level method. The test is based on IEC 60512-2-1. The object of this test is to define a standard test method to measure the electrical resistance across a pair of mated contacts or a contact with a measuring gauge. The contact resistance is considered a benchmark for the quality of a cordset. By measuring before and after testing, the reliability of the contact is verified according the requirements of the standard.
Environmental and durability tests
- Climate conditioning: heat, cold, humidity, temperature shock
- Corrosion conditioning:
- Salt spray test
- Kesternich test (SO2)
- Condensation climate
- Flowing mixed gas
- Vibration tests
- Sinusoidal vibrations
- Resonance search
- Mechanical shock
- Broadband noise
- Tests for degree of protection (IP classification)
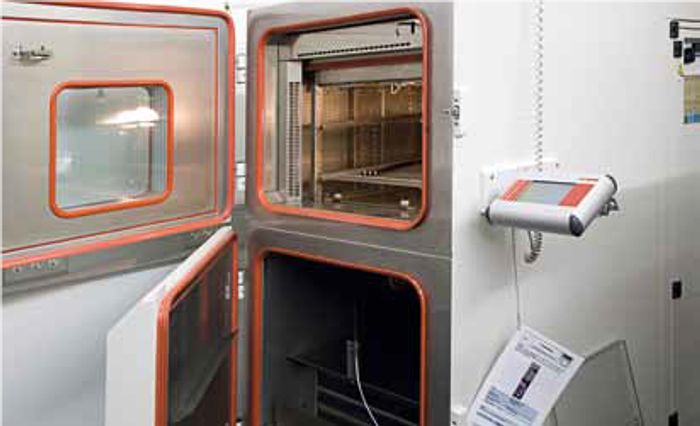

Rapid change of temperature
- IEC 60512-11-4
- The test is performed to find out whether components are able to withstand a rapid air temperature change as could occur during storage, transporting and when in use.
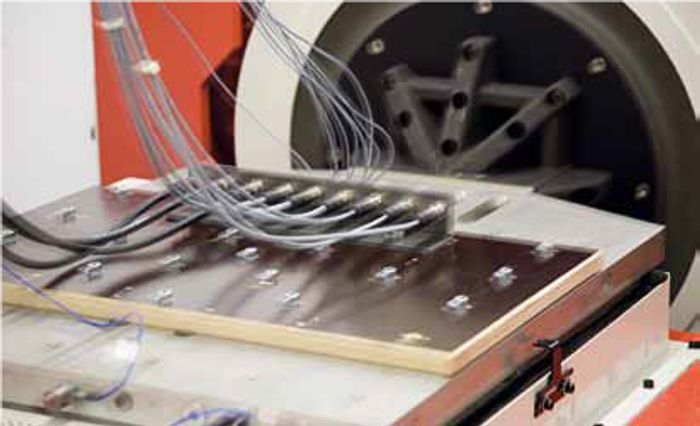

Vibration tests
- IEC 60068-2-6
- The vibration of an electrical connection is verified with this test. Various vibrations are applied to the test object to simulate rotating, pulsating or oscillating forces.
- The test objects are subjected to different, high frequencies and accelerations forces in all three dimensions (xyz).
- The test objects may not incur any damages that would inhibit any further use or the constant electrical values.
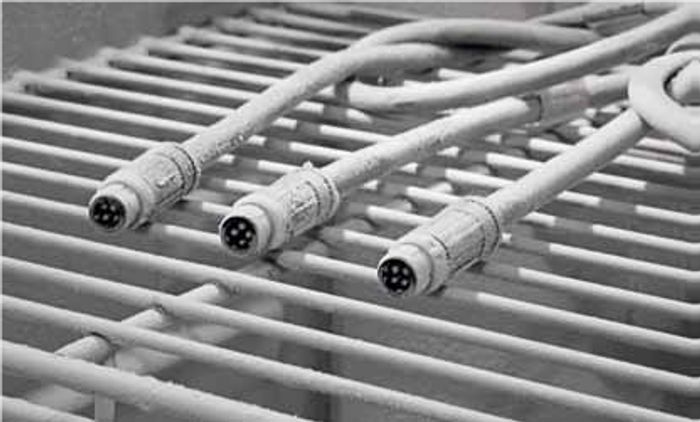

Climatic test - cold
- IEC 60512-11-10
- Components need to be reliable in extremely cold environments. For that reason, this test is performed to determine how well components are able to endure cold conditions.
Certification and special tests
- Bending value
- Stress corrosion cracking
- Inflammability classification
- Glow-wire test
- Relaxation
- RoHS conformity
- Industry and country-specific certifications
- Strain relief
- Jacket retention
