
Surge protection application examples
Look at three examples of surge protection applications to learn how to easily calculate the voltage protection level in the electrical system.
As described, the partial voltages of all connecting parts between the line conductor (terminal point A) and the protective conductor (terminal point B) must be added to the actual voltage protection level of the surge protective device (SPD).
We have performed this calculation for the following three examples.
The voltage drop over the corresponding cables has been taken from the table for the “Voltage drop depending on the geometry”.

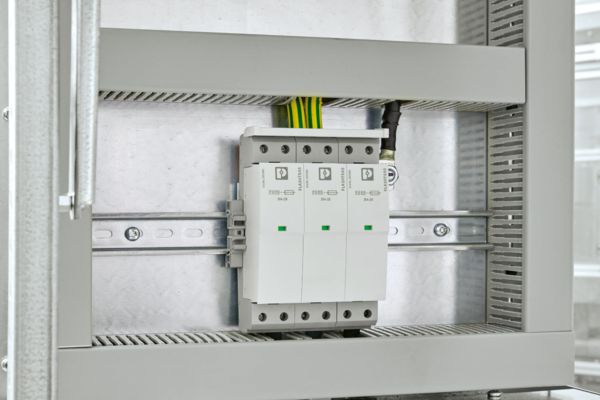
FLT-SEC-HYBRID above the circuit breaker
1. Installation: Above the circuit breaker
Installation is located above the circuit breaker on a grounded mounting plate, which is a considerable distance away from the PEN rail below it.
Note:
Install a direct cable connection from the protective device to the PEN rail, parallel to the connection via the mounting plate. This connection does not increase the voltage protection level of the SPD combination, but is prescribed by DIN VDE 0100-534.
Effective voltage protection level, example 1
With a voltage protection level of 8.2 kV, protection in accordance with overvoltage category IV for switching devices in 230/400 V networks cannot be maintained.
| Length in cm | Partial current in kA | Voltage drop in kV | |
|---|---|---|---|
| PEN connection from SPD to mounting plate | 15 | 75 | 1.1 |
| PEN connection via mounting plate | 115 | 75 | 3.5 |
| PEN connection from mounting plate to PEN rail | 15 | 75 | 1.1 |
| L1-L3 connection | 40 | 25 | 1.0 |
| SPD (voltage protection level) | - | 25 | 1.5 |
| Overall voltage protection level | 8.2 |

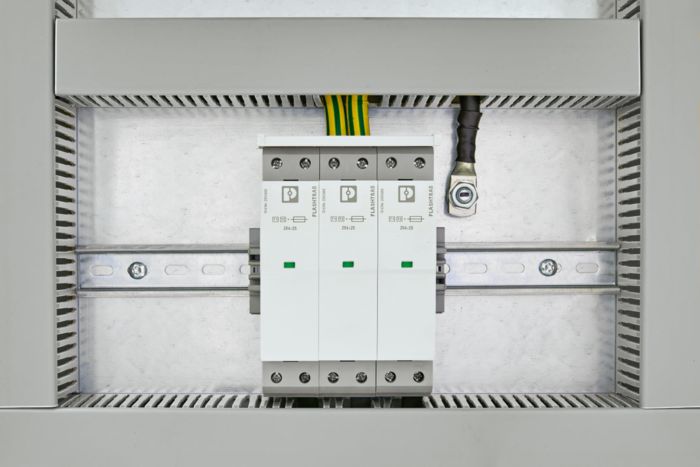
FLT-SEC-HYBRID in the main distribution
2. Installation: Below the circuit breaker
The SPD is installed below the circuit breaker.
For this installation variant, the distance to the protective conductor is relatively short.
Effective voltage protection level, example 2
With a voltage protection level of 4 kV, protection in accordance with overvoltage category III for switching devices in 230/400 V networks can be maintained.
| Length in cm | Partial current in kA | Voltage drop in kV | |
|---|---|---|---|
| PEN connection from SPD to PEN rail | 20 | 75 | 1.5 |
| L1-L3 connection | 40 | 25 | 1.0 |
| SPD (voltage protection level) | - | 25 | 1.5 |
| Overall voltage protection level | 4.0 |
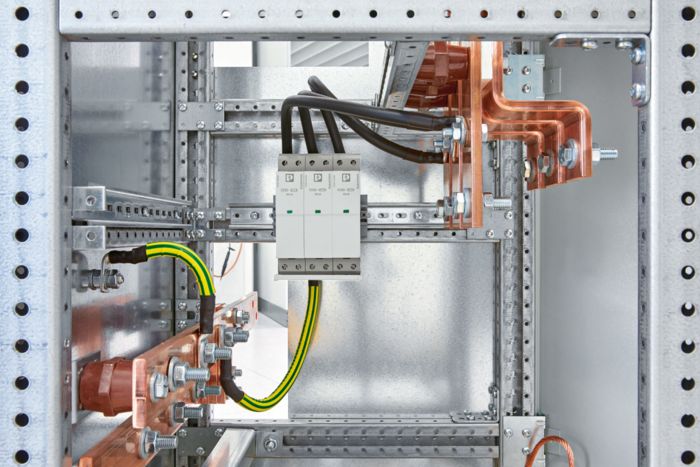
Calculation of the voltage protection level
3. Installation: Below the circuit breaker
The SPD is installed below the circuit breaker with optimized PEN connection.
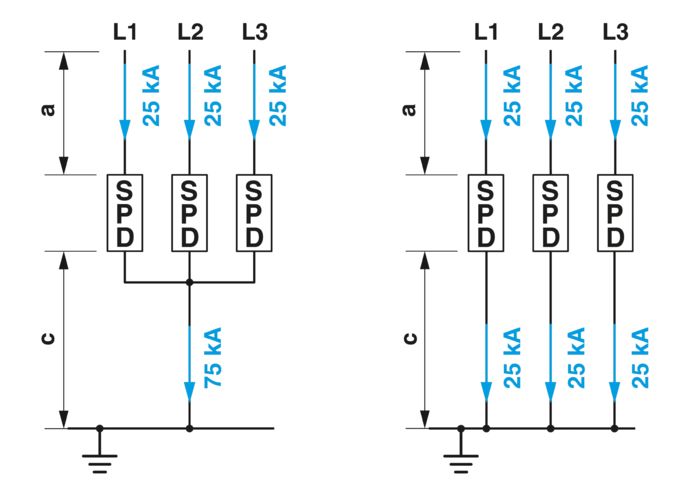
Examples 1 and 2 clearly show that when optimizing the voltage protection level, the focus should be on the connection from the SPD to the PEN rail. The shorter this connection is, the better the voltage protection level. In examples 1 and 2, the influence of the PEN connection is three times higher than the connections to active conductors L1, L2, and L3.
Instead of using one cable to implement the connection to the PEN rail, another option is to use a separate cable for each position, i.e., three individual cables. In this case, the partial current flowing through the cables is just 25 kA and not 75 kA. Accordingly, the voltage drop is then also just a third.
Effective voltage protection level, example 3
With a voltage protection level of 2.5 kV, protection in accordance with overvoltage category II for switching devices in 230/400 V networks can be maintained.
| Length in cm | Partial current in kA | Voltage drop in kV | |
|---|---|---|---|
| PEN connection from SPD to PEN rail | 10 | 25 | 0.25 |
| L1-L3 connection | 10 | 25 | 0.75 |
| SPD (voltage protection level) | - | 25 | 1.5 |
| Overall voltage protection level | 2.5 |
