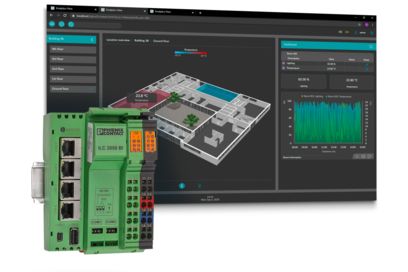
Merging production automation and building automation By coupling the factory automation and building technology sectors, we are able to control the energy consumption of production at the Bad Pyrmont site.

The challenge
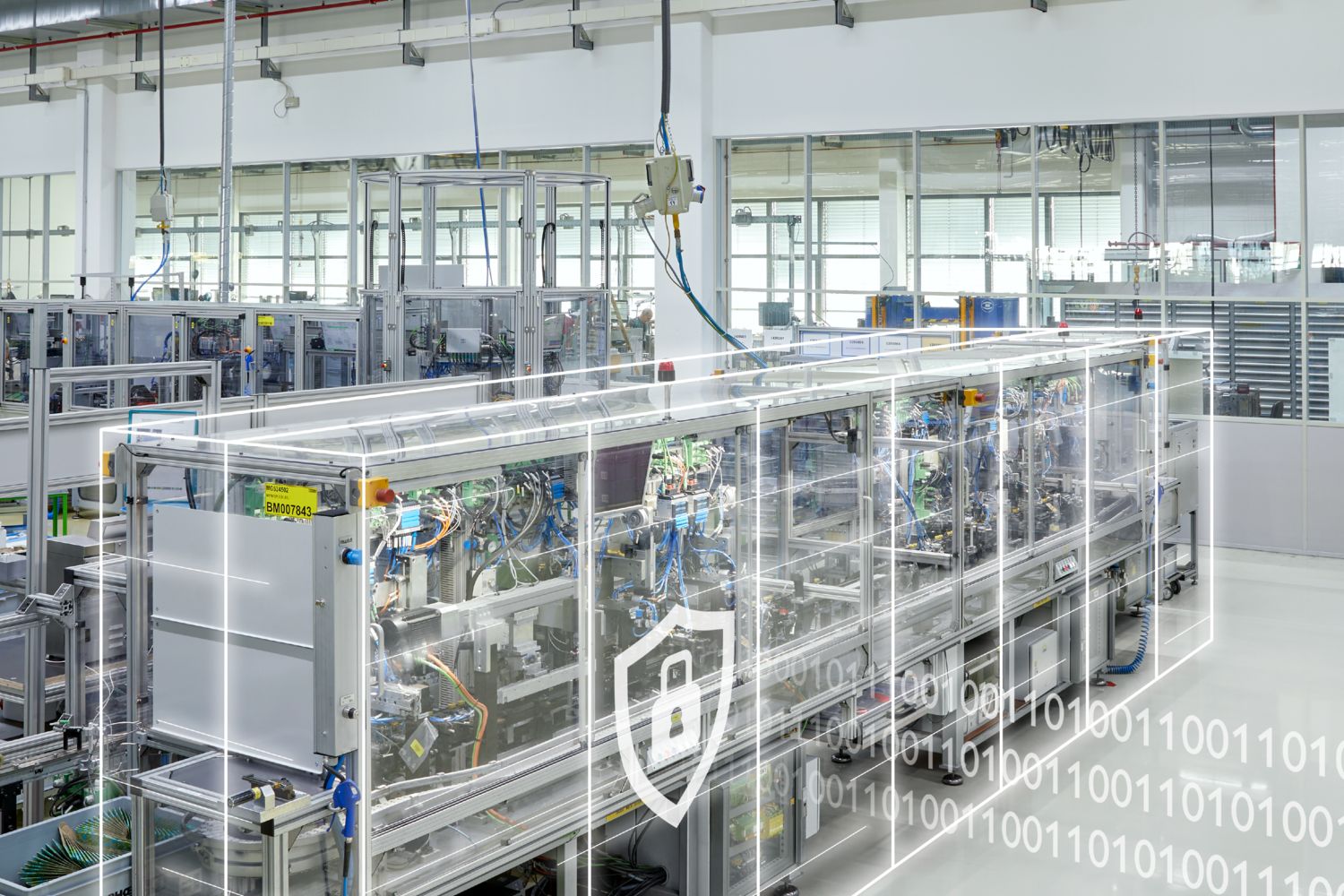

Factory and building networked in depth
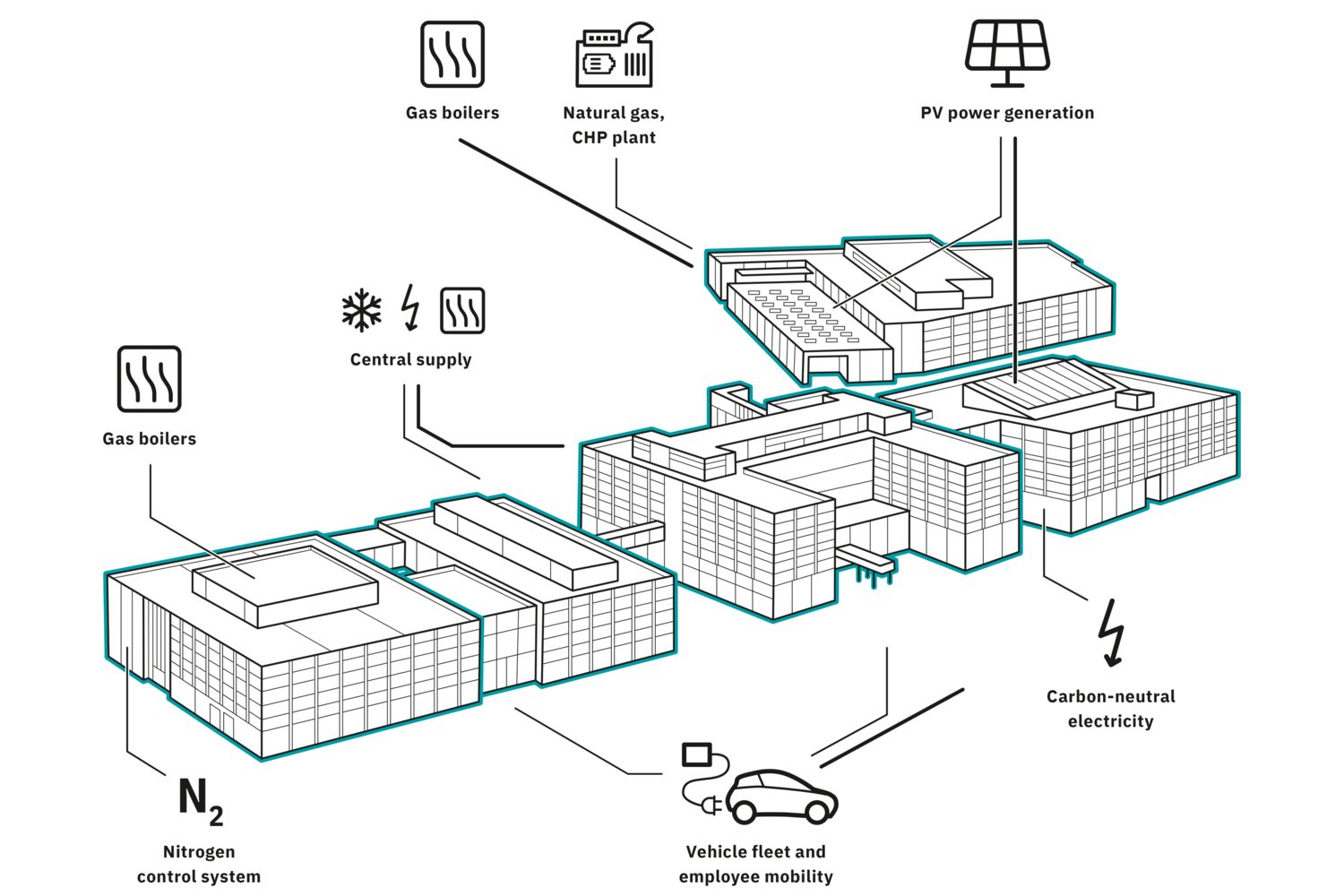
The factory was built in 1996 and has grown significantly in recent years. The challenge was to implement changes in terms of digitalization, increasing efficiency, and sustainability during ongoing operation. Phoenix Contact embarked on this new approach in 2017 as part of a company-wide strategy project. The digital transformation was seen as a fundamental change that required a rethink within the organization. The basis for this was the creation of a digital twin for over 10,000 products and the development of an infrastructure that is available worldwide. Instead of a centralized system, Phoenix Contact relies on a microservice architecture in which the individual application processes communicate with each other via interfaces. The aim was to make intelligent use of the 66,000 or so data points in production, to optimize processes, and to implement active sector coupling in the pursuit of a sustainable future. To do this, the production and building sectors were also networked not only in terms of performance, but also in terms of communication.
The solution

Moving a step closer to the 1.5°C target with digitalization
Sustainability is an essential part of Phoenix Contact’s corporate strategy. With the vision of the All Electric Society, Phoenix Contact is pursuing the goal of creating a sustainable world with solutions and technologies for electrification, networking, and automation. The All Electric Society describes a world in which renewable energy is not only generated and utilized consistently, but also the primary energy requirement is reduced through efficiency measures. Digitalization is an essential building block for the vision of the All Electric Society. With sector coupling, energy flows can be combined across industry boundaries and taken into consideration holistically. The goal is to make energy sufficiently available everywhere – at the right time, in the right place. The intelligent interaction between production and buildings at the Bad Pyrmont site is a real-life example of sector coupling being used in practice in existing facilities.
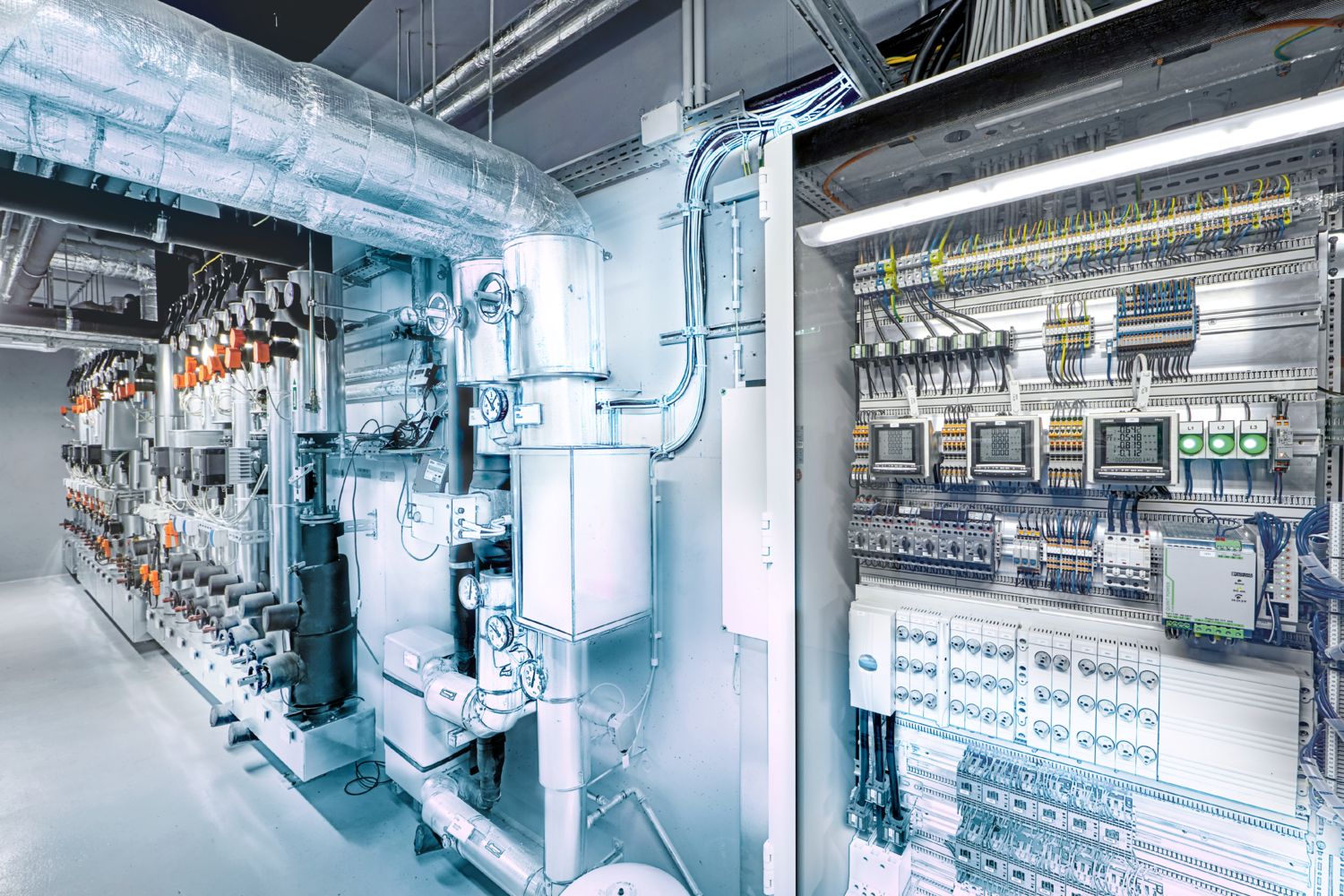

Energy optimization of the Bad Pyrmont production site
Data serves as the basis for comprehensive automation and networking. In order for all sectors to speak the same language, digitalization, data interfaces, and harmonized data formats are required, which enable standardized communication between classic building technology and production.
Your advantages
- Consistent data and information flows
- Resource-efficient and reliable production
- Sustainable power supply
- Comprehensive optimization for climate protection
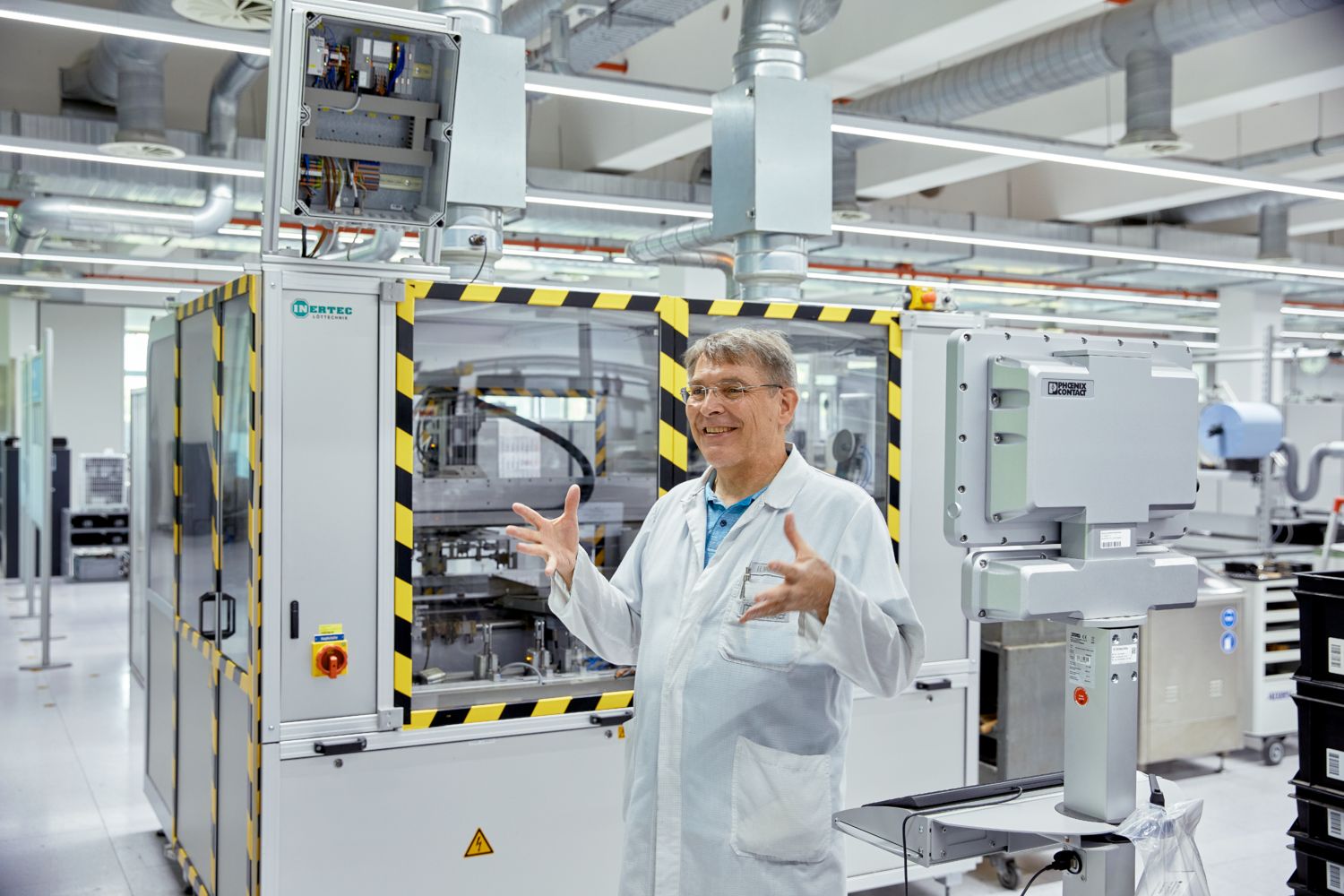

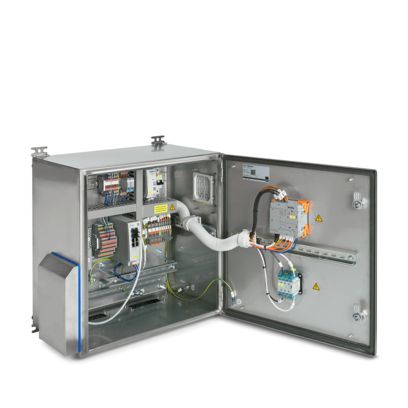
Data Collection Box: Data is the key
The Phoenix Contact production facility in Bad Pyrmont, the PLCnext Factory, obtains information via Data Collection Boxes. These boxes collect, for example, current consumption or data from I/O systems that are connected to 15 to 20 sensors per machine. The data is analyzed and evaluated using the open PLCnext Technology Ecosystem and an AI-based learning algorithm in order to detect and rectify deviations such as energy losses in the system or anomalies in the process.
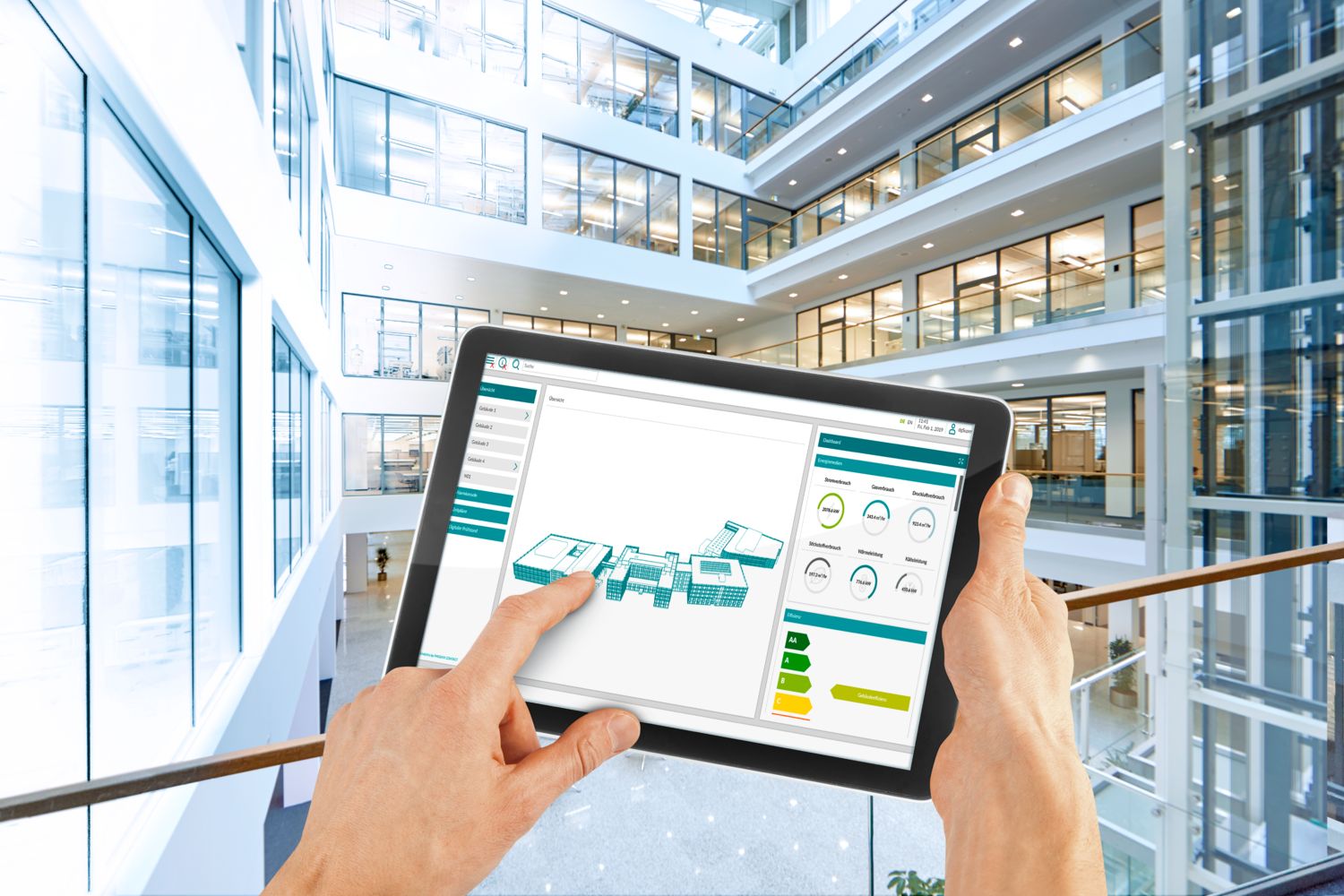

Open ecosystem meets IoT-based building management system
The solution of the open PLCnext Technology Ecosystem merges with our IoT-based building management system Emalytics – the platform for all applications and processes in the building. By taking into account the entire process chain and the intelligent interaction of production and buildings, we create new opportunities to increase added value and even reduce building operating costs by around 50%. This merging of production automation and building automation means that the infrastructure, such as the ventilation system, lighting, cold water, and compressed air, is only made available to production when it is actually needed – on a demand-oriented and automated basis. In addition to the optimization of consumption data, the intelligent use of renewable energy in production and in buildings is equally important. By combining the open PLCnext Technology Ecosystem, Emalytics, and the use of a microservice architecture, we can respond flexibly to future requirements. This puts us in an ideal position to achieve our sustainability goals and a carbon-neutral footprint.
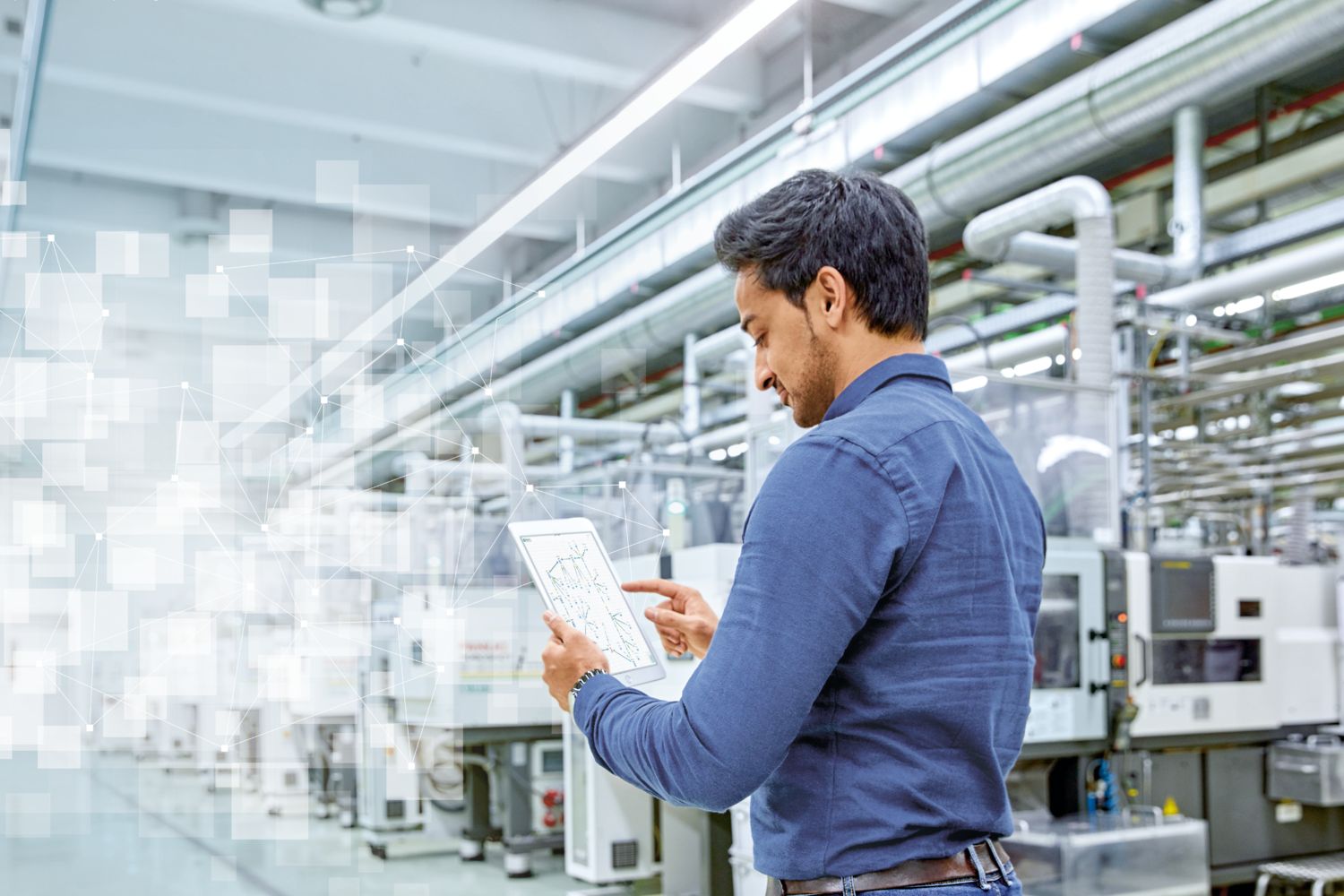

Manufacturing X in the Digital Factory
With the Mindset of Manufacturing X to a new way of thinking in the Digital Factory – the Asset Administration Shell (ASS), as a digital twin of Industry 4.0, enables seamless integration that also incorporates the OPC UA communication standard. The basic architecture is the same for everyone and interoperable. This is the basis for common functions that can be used by everyone, thus enabling a shared industrial data space. The individual application processes communicate with each other via interfaces. To do this, we had to work very transparently within the organization, learn from each other, and leverage synergies. With this solution, we are able to strengthen our competitive edge because our digital innovations and value creation in solution systems and ecosystems are a major advantage. We are strengthening our resilience because we are able to optimize ourselves more rapidly and respond to malfunctions faster. We can also better map regulatory requirements, such as those relating to the EU Digital Product Passport or carbon footprint, the circular economy, or transparency in supply chains.
Around 200 kg of CO₂ saved per year
The entire production facility, which now employees 550 people and assembles 1.8 million components each day, exemplifies efficiency and speed. One success factor is that every single workstation in the PLCnext Factory is now networked. The system accesses live data, can collect key figures from the production lines, and use these to make improvements. Approximately 2.7 million data points per day and therefore 270 TB of operating and process data per year are aggregated and evaluated. In three years, we were able to increase our productivity by 30% and at the same time save around 30% energy. The improvements made in production result in savings of around 1.5 million euros per year. The building independently controls energy consumption and thus ensures savings of approx. 500 kWh (approx. 200 kg of CO₂).
Contact

Products

Still haven’t found the right product?
Feel free to contact us. We will consult with you to find the ideal solution together.
Summary
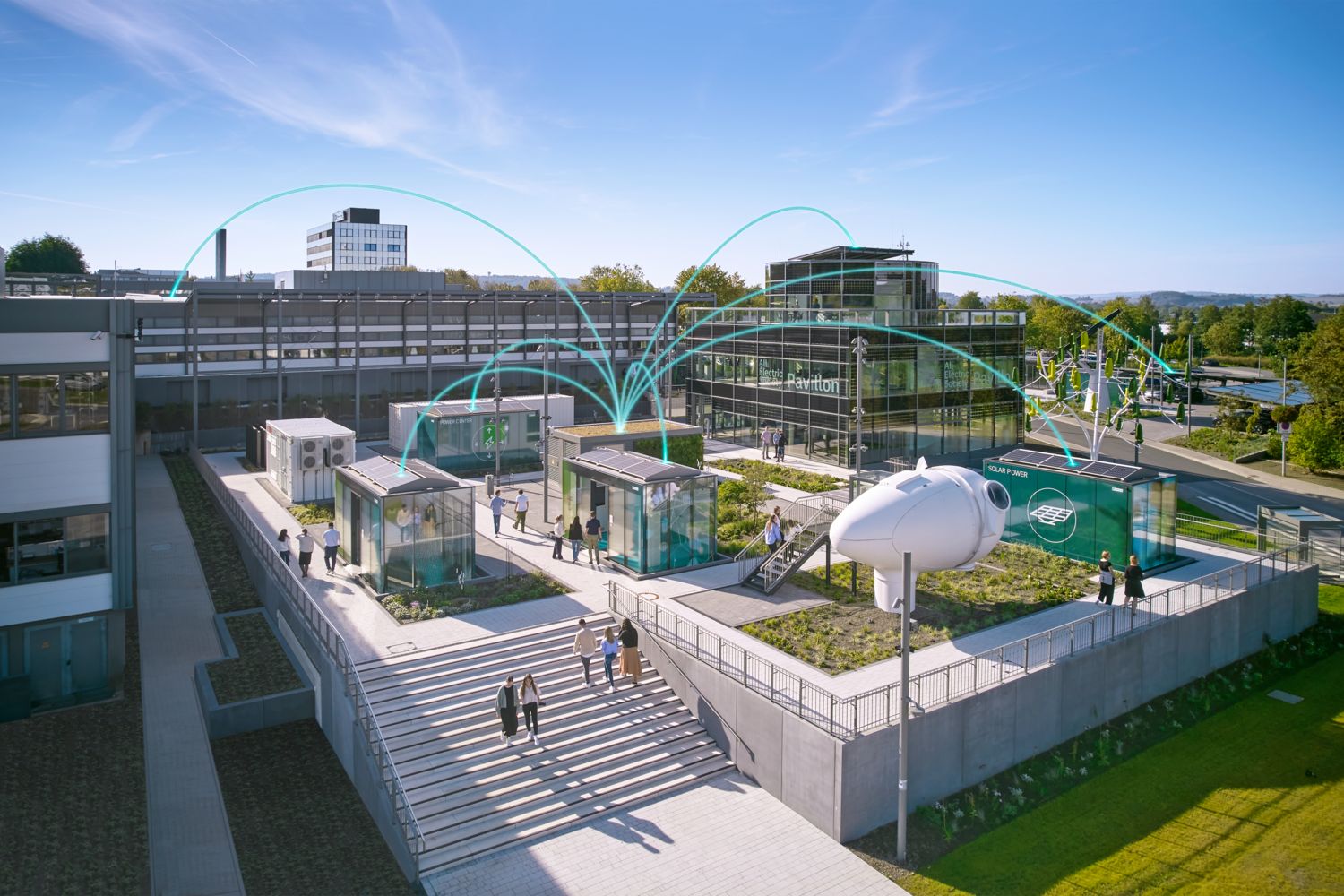

Outlook for a sustainable future
By utilizing our in-house products and solutions for electrification, networking, and automation in our PLCnext Factory, the customer receives a product with a demonstrably reduced carbon footprint. The intelligent interaction between the building and factory also enables the future-proof transformation of all trades towards a more sustainable and productive factory. Based on trust, data transparency, and flexibility, the corporate divisions work daily to optimize cross-sector efficient operations. The building management system is connected to the production area as well as to the charging station of the company’s e-fleet and a battery storage system that is powered by energy generated in-house. The battery can also be charged from power drawn from the local power grid, but it is ideally supplied by the in-house photovoltaic system. Through cooperation with municipal utilities, sewage treatment plants, and leveraging synergies throughout the district (e.g., heating network), we are moving a step closer to the 1.5°C target every day. At the same time, we offer our customers these tried and tested solutions for the digitalization of their own factories and thus provide true proof of concept. Our motivation is to drive innovation towards an All Electric Society.