IO-Link Safety
What is IO-Link Safety?
IO-Link Safety is the extension of the globally standardized IO-Link communication to include the requirements on functional safety. As a part of this, IO-Link Safety enables consistent communication in automation systems, from the control level right through to the safety-related sensors and actuators in the field.
With this technology extension, users also benefit from typical IO-Link advantages in the field of functional safety, such as simple configuration via IODD and fast device replacement. This creates a universal, simple, and cost-effective safety solution. The interaction of IO-Link and IO-Link Safety promises new, manufacturer-independent machine and system concepts.
Advantages of IO-Link Safety
IO-Link Safety combines proven advantages of the IO-Link technology with the field of functional safety:
- Increase productivity through detailed condition data
- Simplify installation, maintenance, and replacement processes with implemented standards
- Increase data availability and accuracy through simple A/D conversion
- Fast configuration with remote diagnostics
- Integrate safety components through the safety functionality
How does IO-Link Safety work?
IO-Link is an open, serial point-to-point communication protocol for connecting sensors and actuators to an automation system.
IO-Link Safety data transmission via black channel
The black channel principle
The IO-Link Safety technology extension is based on the idea of the black channel principle. The principle enables secure communication via the standardized IO-Link communication medium. In addition, safety-related signals and standard signals can be transmitted together in one communication channel.
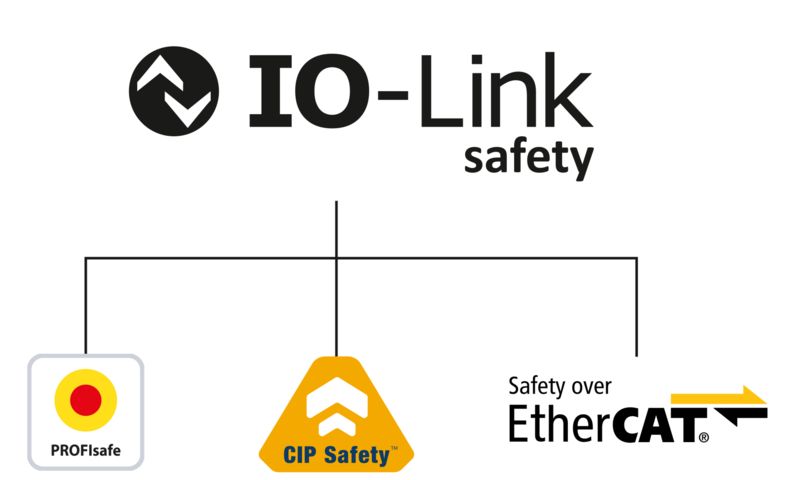
Safe and fieldbus-independent communication via IO-Link Safety
Fieldbus-independent communication
Thanks to uniform communication via IO-Link Safety, the large number of IO-Link devices used can be reduced in the future. Fieldbus-independent communication therefore also simplifies purchasing and saves warehousing costs.
System architecture
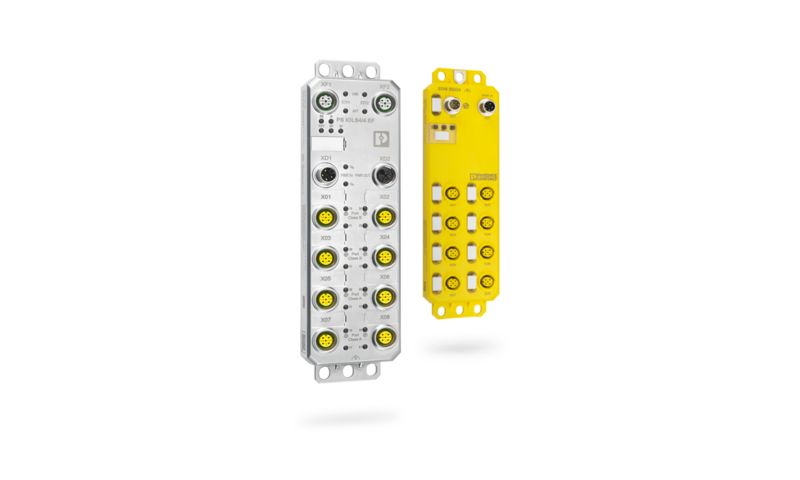
The architecture of an IO-Link Safety system consists of a controller, an IO-Link Safety-capable master, and one or more devices. A safety controller is required in order to process safety data.
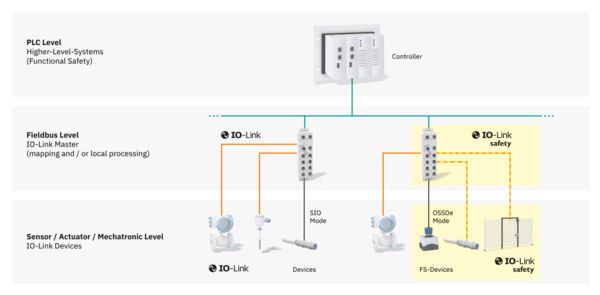

IO-Link Safety master and IO-Link Safety device
IO-Link Safety master
The IO-Link Safety master is the interface to the higher-level safety controller and enables safe communication with the connected IO-Link devices.
IO-Link Safety devices
Thanks to the IO-Link Safety technology extension, safety-related devices such as safety sensors, safe sensors via OSSDs, safe actuators, and mixed safety devices (e.g., mechatronic devices) can be connected to the IO-Link Safety master alongside the classic standard IO-Link devices.
IO-Link Safety in application
The following application examples illustrate how versatile and useful IO-Link Safety can be in various industries.

Production line with robots
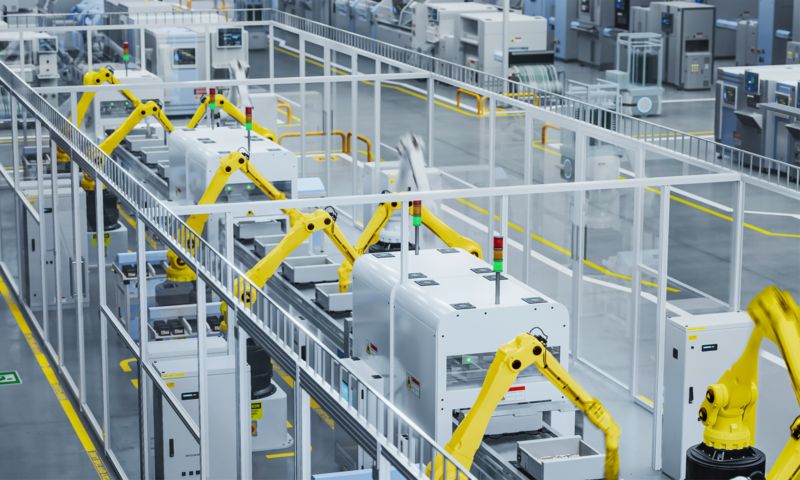
Safe monitoring of robot positions
In a production line, a robot provides support in picking raw materials for manufacturing a product.
IO-Link Safety enables the cost-effective and safe monitoring of robot positions. Numerous diagnostic options enable maintenance planning, error detection, and troubleshooting. With the IO-Link data storage function, it is easy to replace a device if it becomes damaged.
The use of standardized cables simplifies wiring.

Master on pneumatic valve terminal
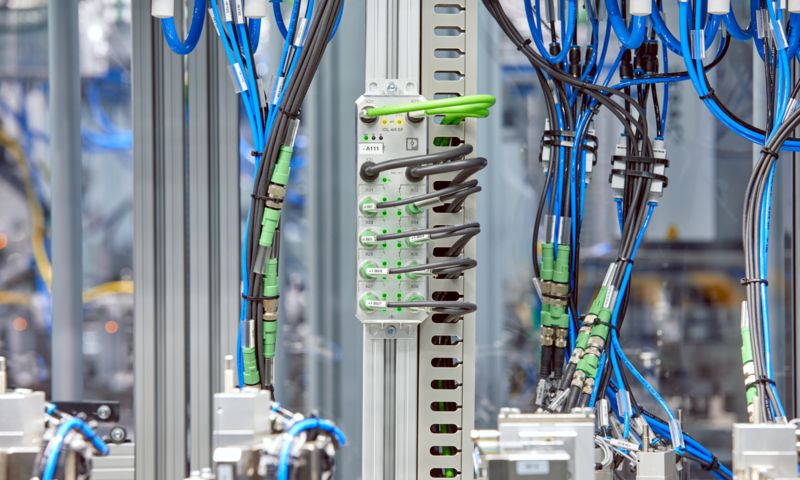
Safe shutdown of pneumatic valve terminals
When actuated, emergency stop buttons should interrupt the supply voltage of the valve terminals and therefore the pneumatic air supply of the cylinders.
IO-Link communication enables full access to the diagnostic messages of the valve terminal. The safety-related shutdown is carried out up to PLe or SIL 3. The connection can also be connected under increased protection conditions in the IP65/IP67 area. The use of the M12 cable with push-pull connection simplifies and optimizes wiring.

IO-Link-Safety white paper
More about IO-Link Safety
Would you like to receive further information on IO-Link Safety?
Learn more in our white paper about:
❯ The structure of IO-Link and IO-Link Safety
❯ IO-Link Safety in the context of functional safety
❯ Changes due to IO-Link Safety

