BC 161,6 OT U11 HS 4C 90 KMGY
-
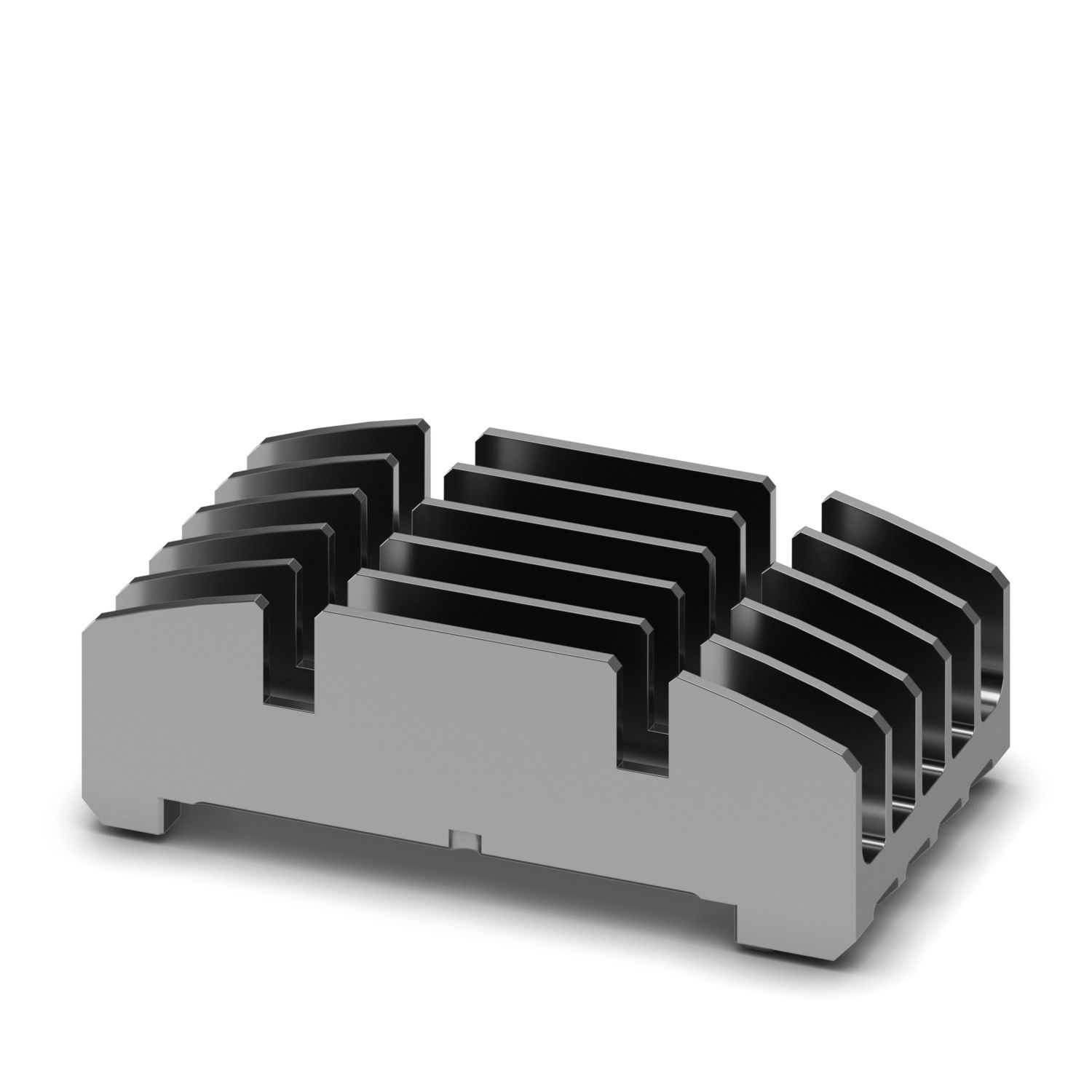
Upper housing part
1756994
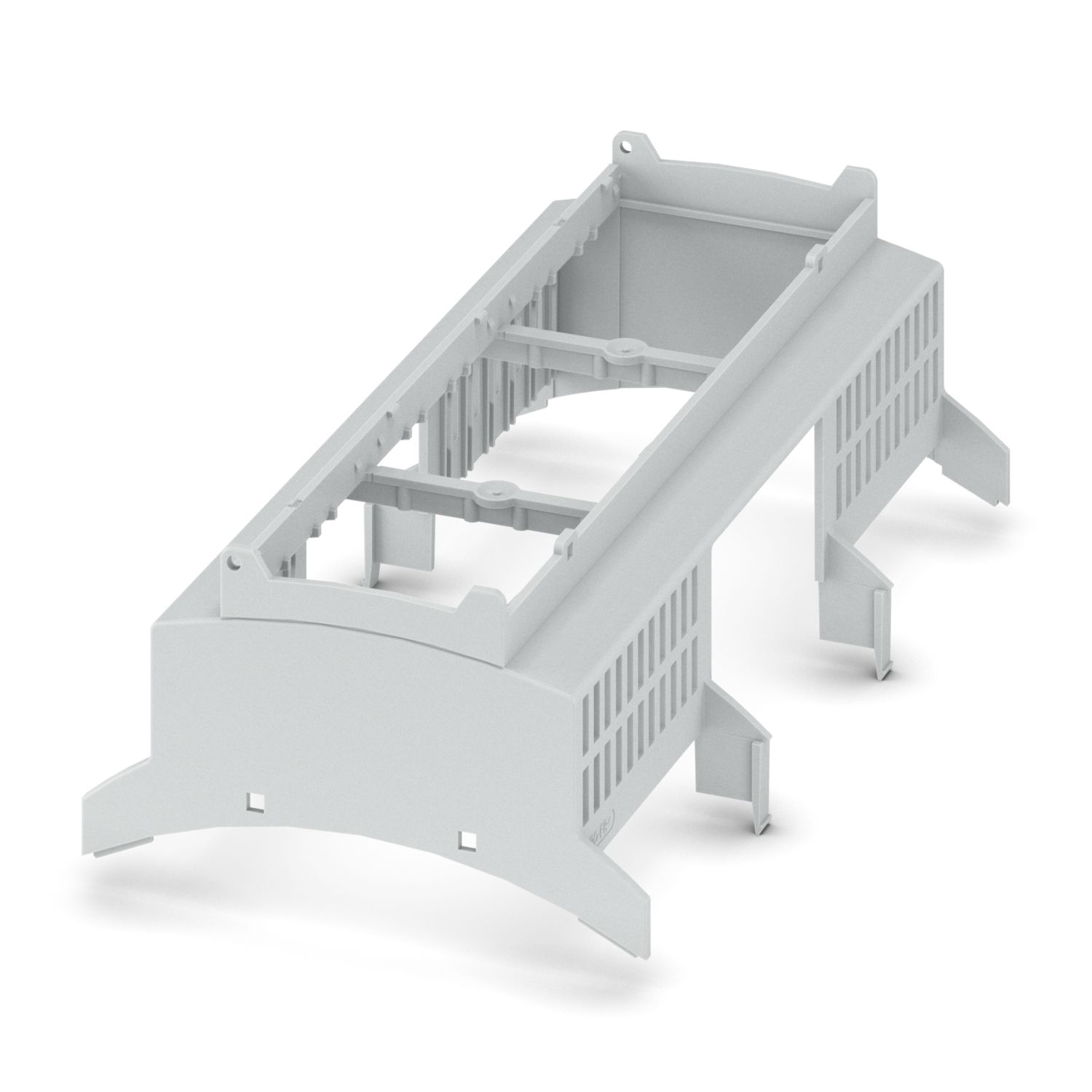
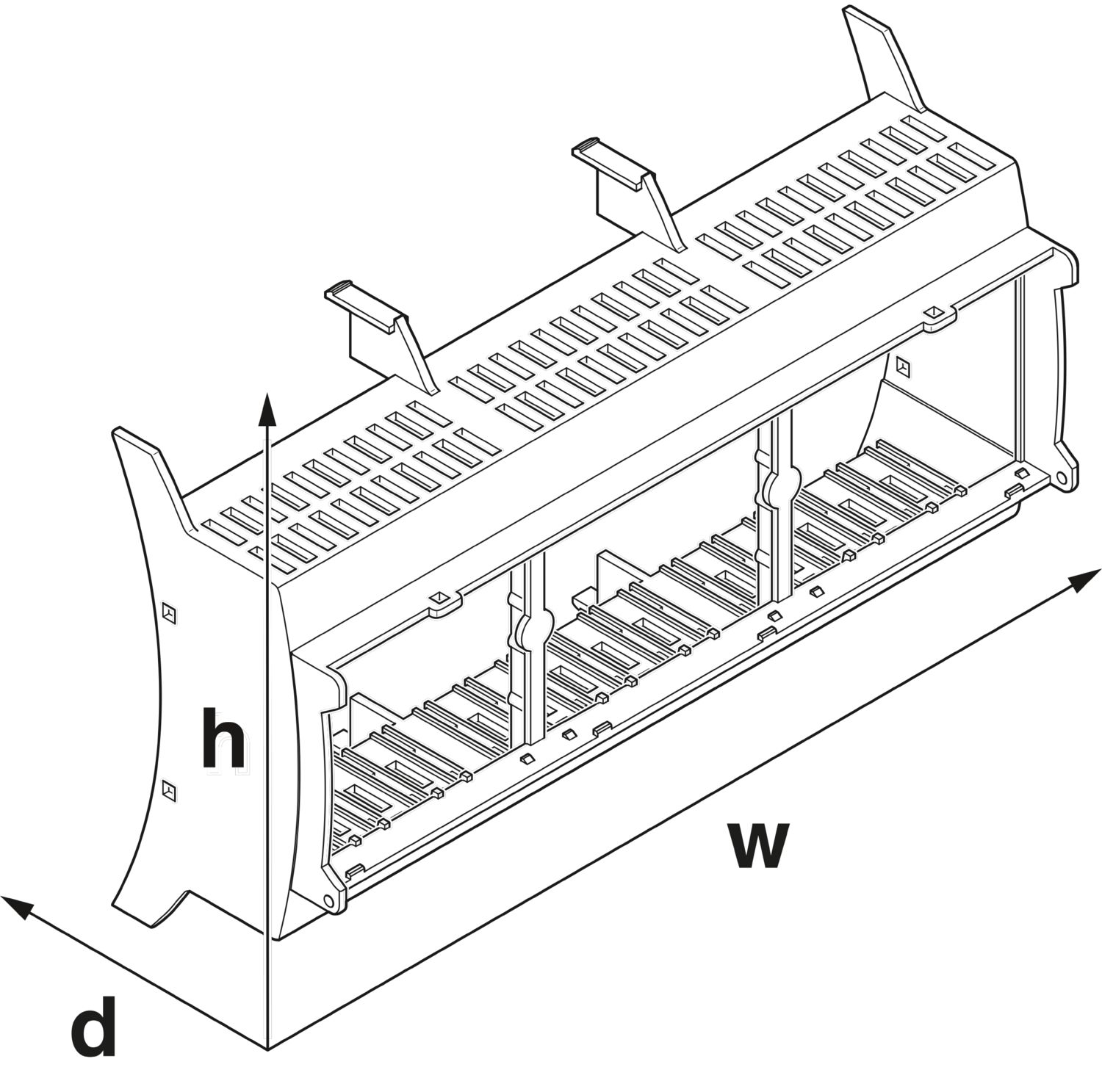
DIN rail housing for use in distribution boards in accordance with DIN 43880, Upper housing part (U11) with vents, Installation depth connection technology: 11.1 mm, width: 161.6 mm, height: 89.7 mm, depth: 54.85 mm, color: light gray (similar RAL 7035)
Product details
Compatible products
Your advantages
Frequently asked questions
What support does Phoenix Contact provide in the area of thermal management?
Phoenix Contact supports you with catalog values, online simulations, personal consultation including simulation services, and (individually adapted) heatsinks.
How are components of different heights and sizes ideally connected to the heatsink?
The optimum thermal connection is implemented by individual adjustments of the heatsink. This is usually done by a milling operation on the heatsink.
What influence does heating have on the reliability of a device?
The maximum temperature has the greatest impact on the reliability and service life of your device. With a temperature increase of 10°C the failure rate is doubled.
Which factors influence the temperature in the housing?
Small and powerful components, high data rates, dust, and insufficient ventilation of the housing are reasons for a high temperature difference compared to the environment.
What information do the power dissipation diagrams provide?
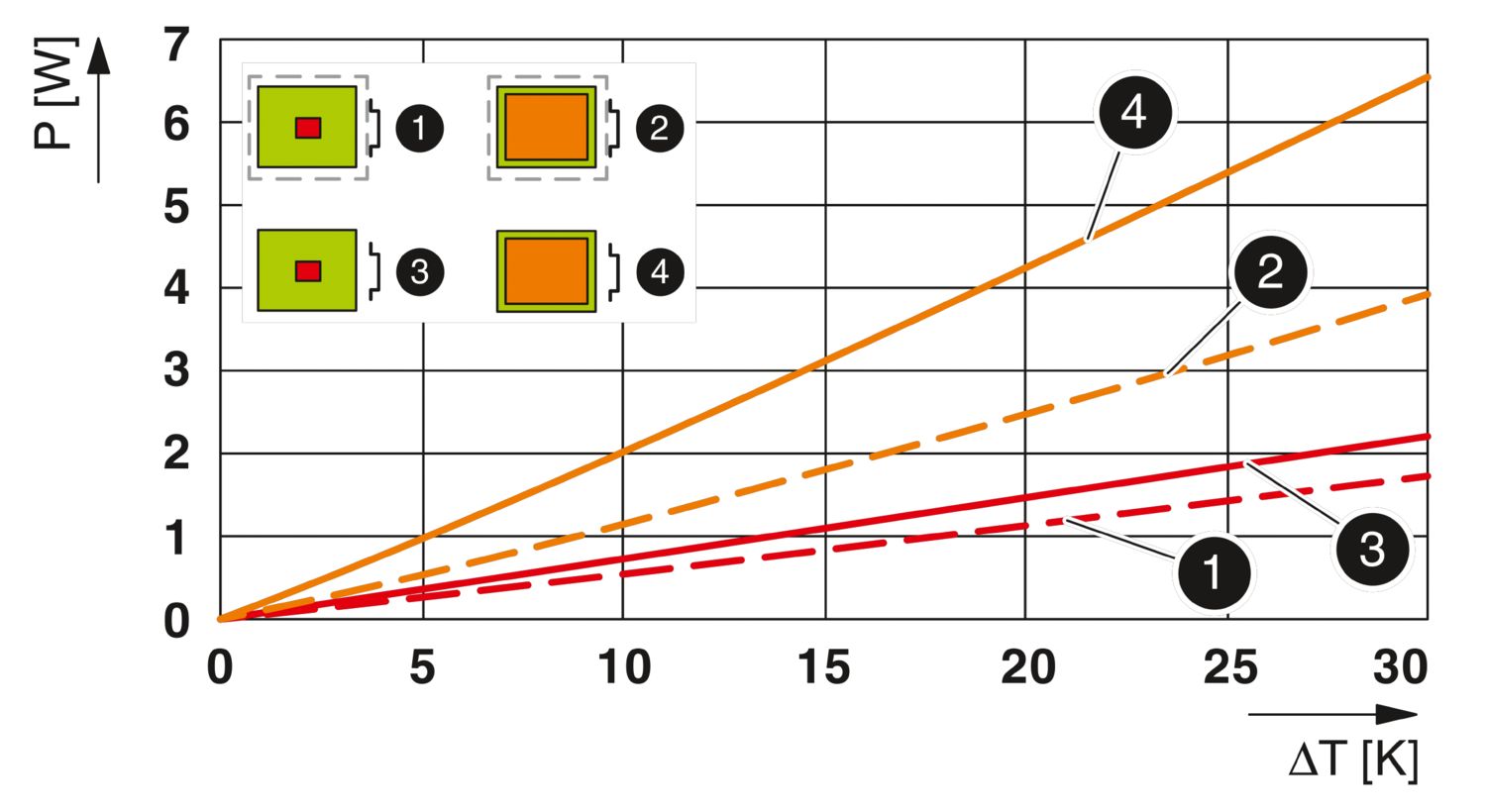
The graphs of the diagrams provide information on which power the components may supply in the respective housing in order not to exceed a temperature difference to the environment. The slope of the straight line describes the thermal conductance of ... View more
The graphs of the diagrams provide information on which power the components may supply in the respective housing in order not to exceed a temperature difference to the environment. The slope of the straight line describes the thermal conductance of the system. The cases shown differ, on the one hand, in that one features full-surface heating while the other features heating of a hotspot of 20 x 20 mm and, on the other hand, in that one has a printed circuit board installed in the housing and one does not have a housing.
View lessHow do heatsinks help dissipate developing heat?
The integrated heatsinks from Phoenix Contact dissipate heat from the hotspot by means of heat conduction via thermally conductive material (TIM). The heatsink releases this heat in the form of radiant energy and via convection between the slats to t... View more
The integrated heatsinks from Phoenix Contact dissipate heat from the hotspot by means of heat conduction via thermally conductive material (TIM). The heatsink releases this heat in the form of radiant energy and via convection between the slats to the environment. The stack effect is utilized, during which the heated air rises and is displaced by cold air.
View lessWhat other options are there for thermal optimization?
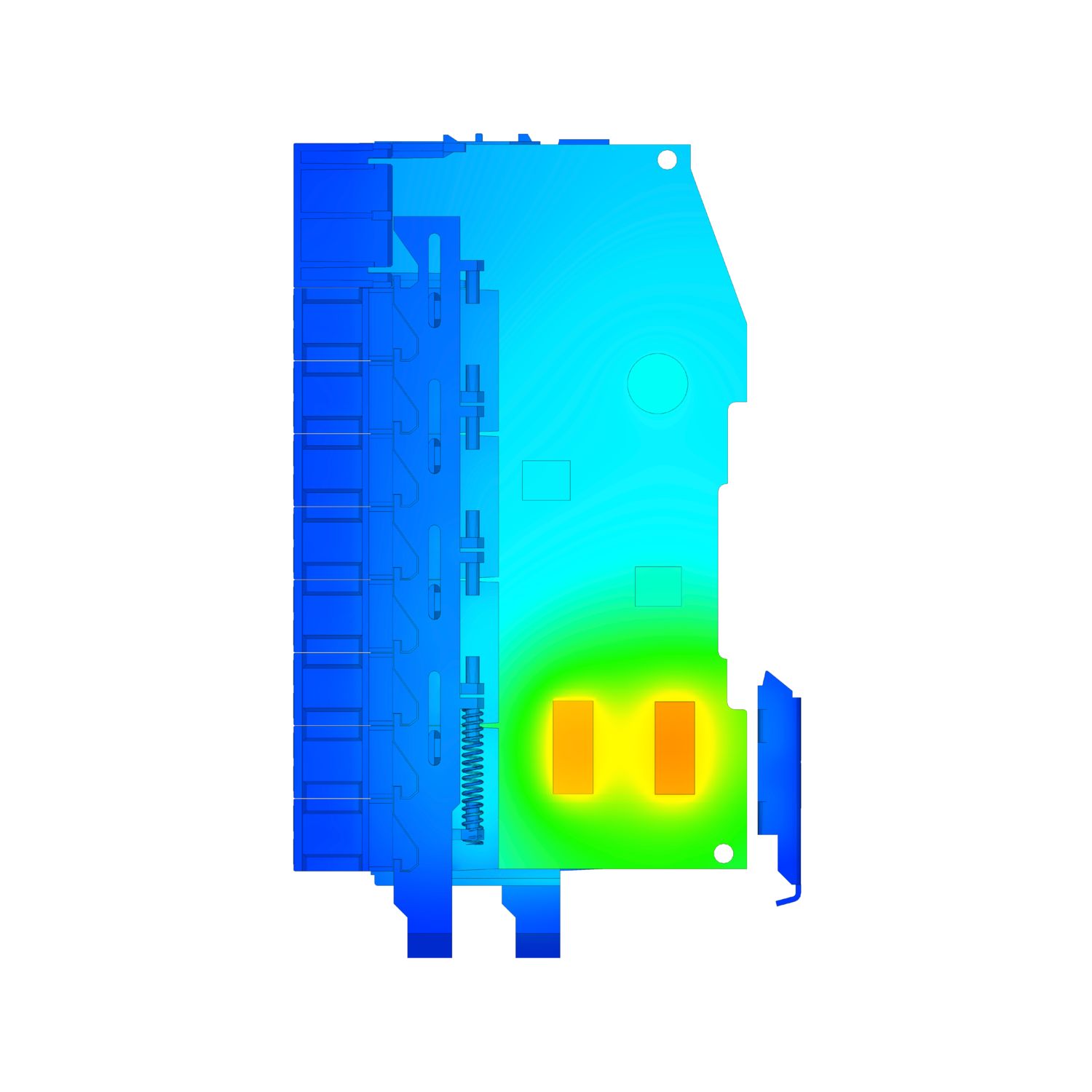
In many cases, rearranging the hotspots or installing vents is sufficient. A simulation of the thermal conditions provides information on which option is best suited.... View more
In many cases, rearranging the hotspots or installing vents is sufficient. A simulation of the thermal conditions provides information on which option is best suited.
View less