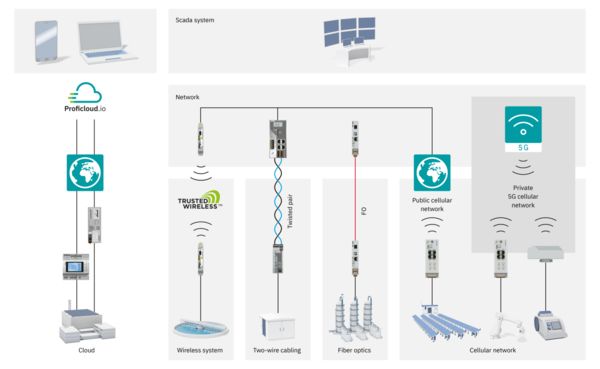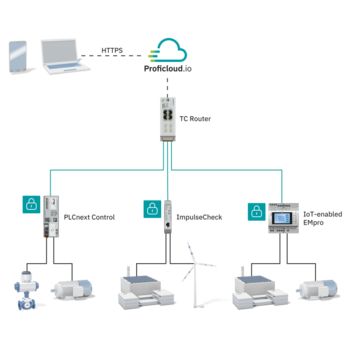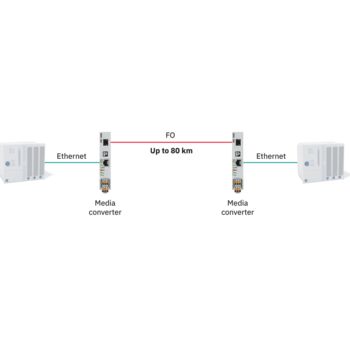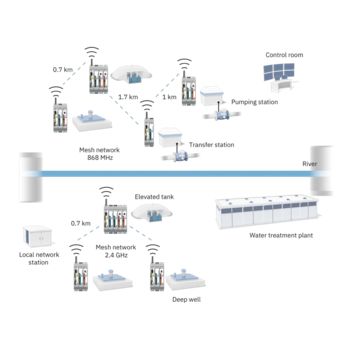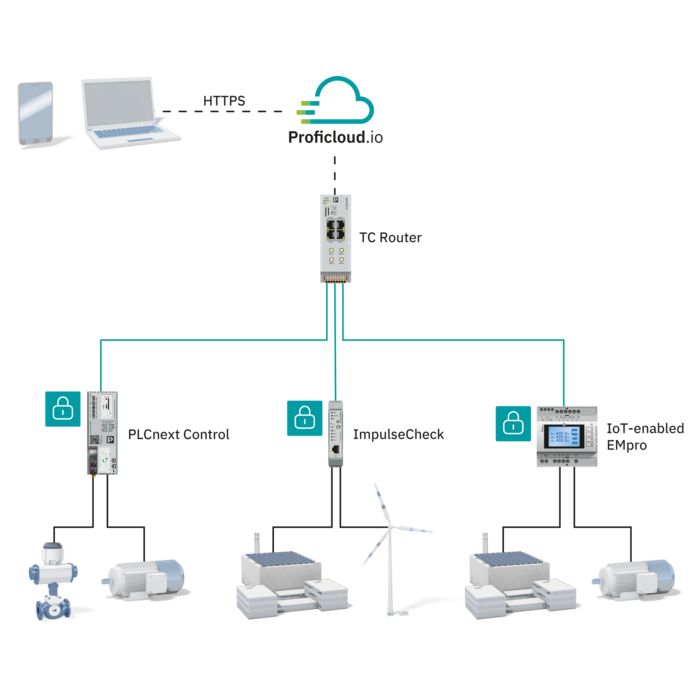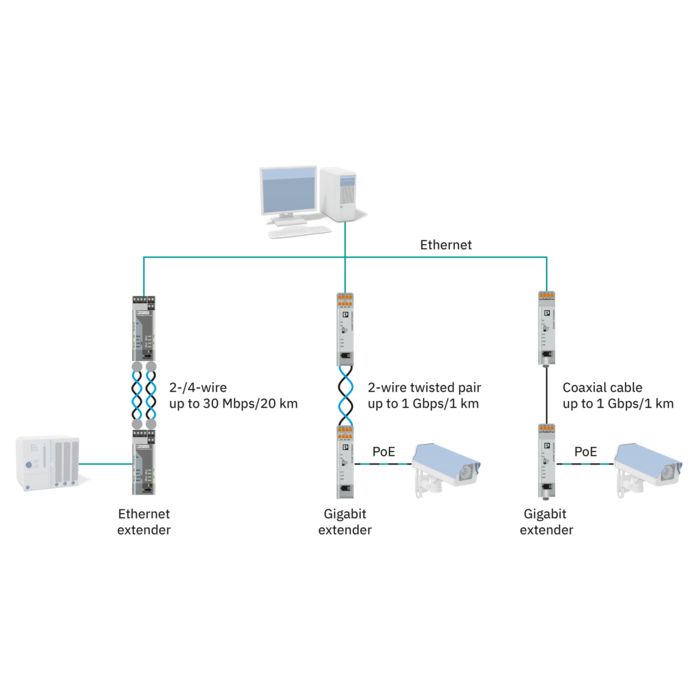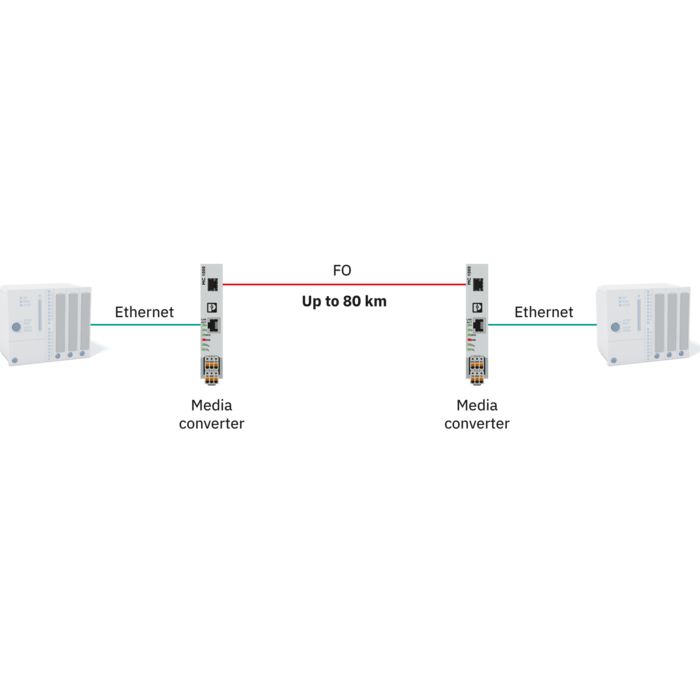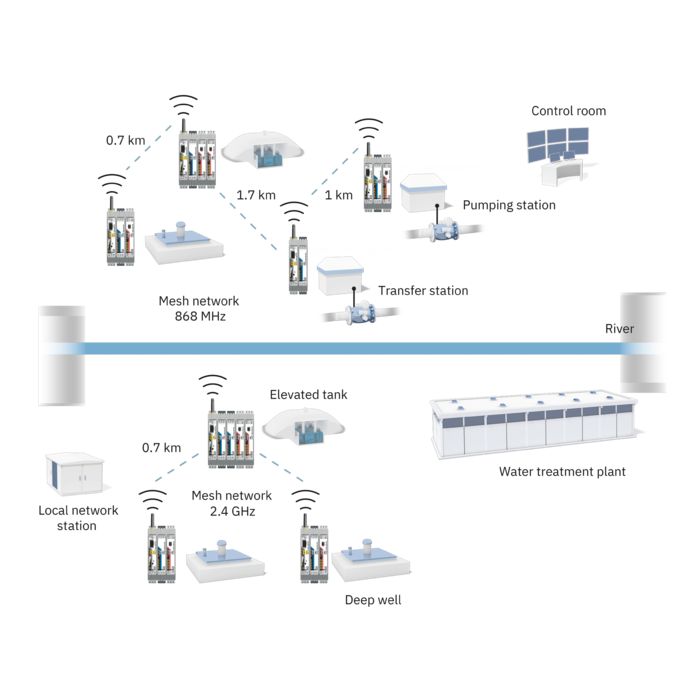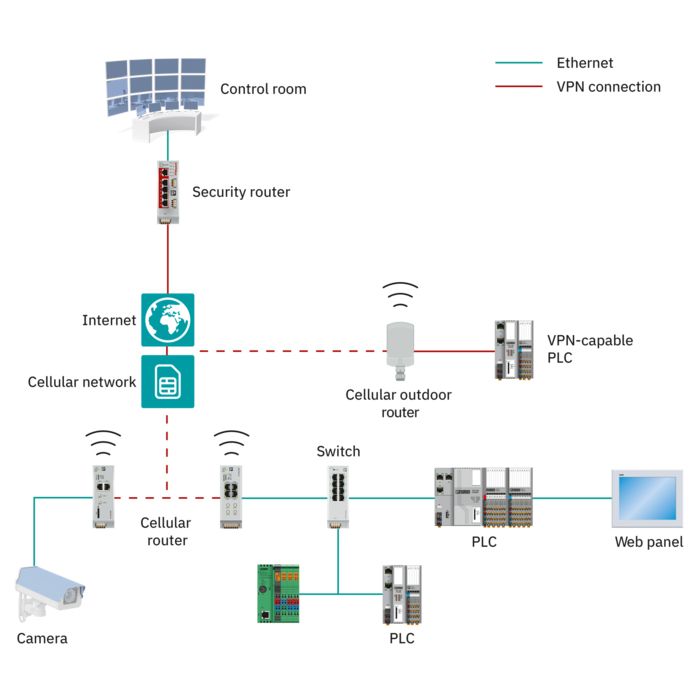
For the continuous acquisition of your process data, Phoenix Contact provides cellular devices that support all technology standards (5G, 4G, 3G, and 2G). With the globally available cellular network, the devices can communicate reliably, even in areas with a weak infrastructure.
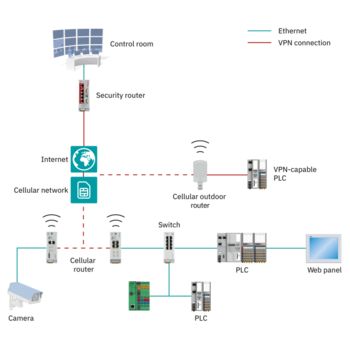
The small remote stations and entire system parks, such as remote pumping stations, can be connected to the control center using methods ranging from SMS messaging, through remote control protocols at low data rates, all the way to broadband VPN connection, depending on the requirements.