Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN) Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN) enables the control and prioritization of data streams in Ethernet networks. The individual requirements such as guaranteed bandwidth, time synchronization, or low latency for individual applications are taken into consideration to ensure the real-time capability of the system.

What is Time-Sensitive Networking?
Time-Sensitive Networking is a set of standards designed to improve the real-time properties of current Ethernet networks. This therefore is comprised of several individual standards that are currently being defined in the TSN Task Group of the IEEE 802.1 standardization organization.
However, Ethernet TSN is not an independent communication protocol. Instead, it defines functions. These functions can in turn be used by different protocols such as OPC UA or PROFINET.

TSN enables a convergence of IT and OT
Advantages and features of the new TSN standard
The data transmission of real-time-critical applications (such as closed-loop controls, signal acquisition in power grids, or motion control) and data-intensive applications (such as video streams or IT systems) is currently implemented in separate networks in order to prevent mutual interference. However, the growing flexibilization and digitalization of work processes require the increasing convergence of IT and OT, and therefore the consolidation of previously separate systems.
By extending and adapting existing Ethernet standards, TSN creates a convergence between information technology (IT) and the industrial operational technology (OT) in industrial networks. This means that both real time-critical data and data-intensive applications (such as video streams) can be implemented via a shared Ethernet cable, without interfering with each other.
How TSN technology works
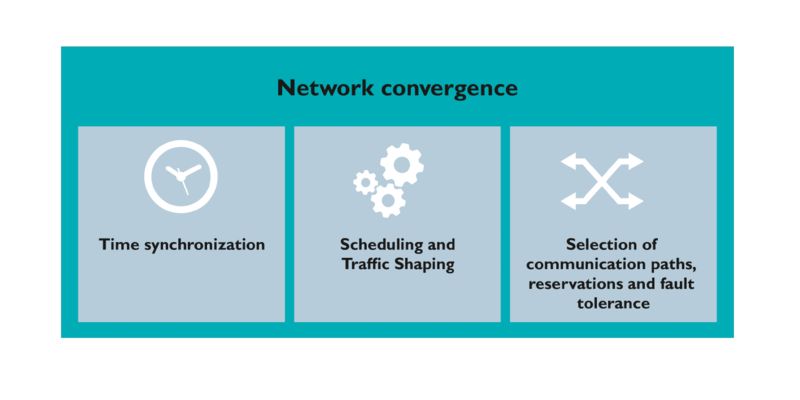
TSN is based on three core mechanisms that are defined in different standards.
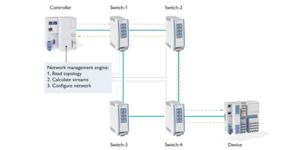
All real-time-critical communication in the network is organized into streams, which are provided with a certain Quality of Service (bandwidth, latency, etc.) based on the requirements and prioritization of the relevant data packet. Streams must be reserved prior to use so that the available bandwidth can be tested in relation to other streams. A network management engine, also known as a centralized network controller or CNC, (e.g., in the controller) reads the topology, calculates the streams, and configures the network accordingly.
Protocols via TSN
Time-Sensitive Networking enables the simultaneous transmission of several automation and IT protocols in one convergent network.
The most commonly discussed protocols here are PROFINET and OPC UA; however, other systems such as CC-Link IE are also specified for use with TSN. To ensure that these protocols do not cause mutual interference in a network, they need to agree on a common profile of how TSN mechanisms are used in the network. This profile is currently being defined in a joint working group for IEC and IEEE under the umbrella of IEC/IEEE 60802-IA.
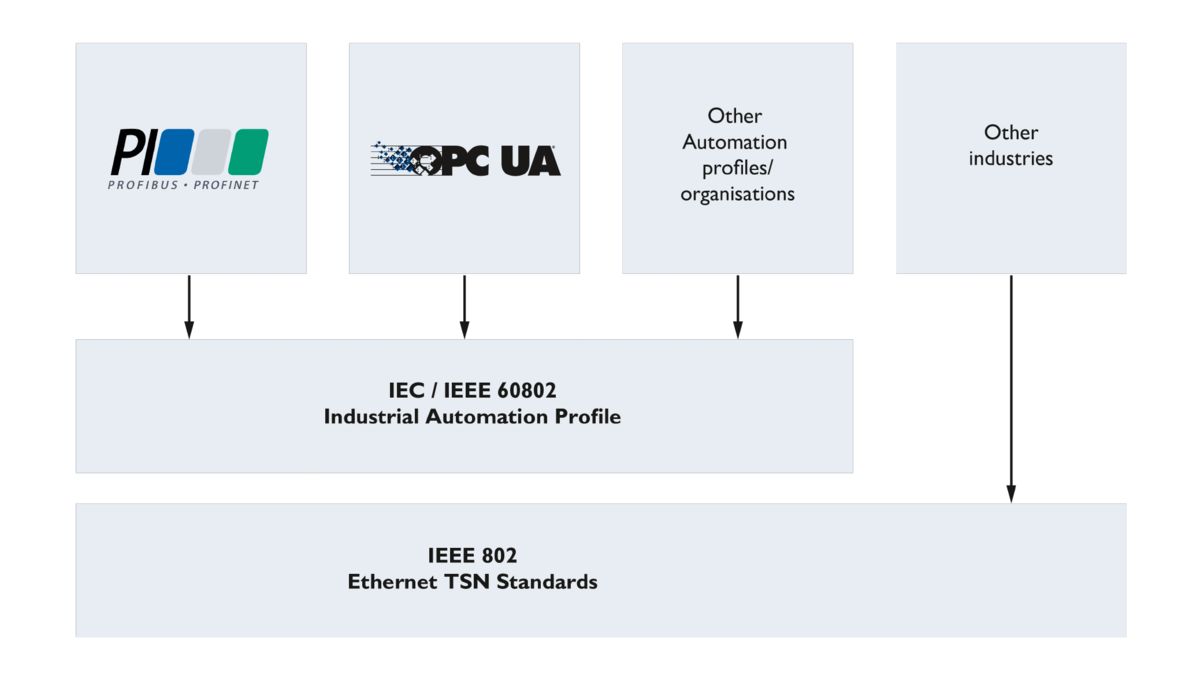
Joint TSN profile in accordance with IEC/IEEE 60802 – IA
The use of TSN standards (“Streams & Configuration”, “Time & Cycle Synchronization”, and “Frame Preemption”) is already specified in version 2.4 or later of the PROFINET standard. The corresponding IEEE standards have been used in such a way that the fundamental properties of PROFINET have been retained. Devices are therefore already being developed with the PROFINET TSN profile and will soon be available on the market.
The Field Level Communication (FLC) Initiative of the OPC Foundation is currently working on the standardization of the OPC UA in combination with TSN. As soon as standardization is complete, corresponding devices will also be developed here that support the OPC UA PubSub in conjunction with TSN.
Our commitment to TSN
Phoenix Contact is involved in all of the relevant standardization organizations, such as the OPC Foundation and PI International, and is actively working on the implementation of the standards defined in IEC/IEEE 60802. In addition, we are already devising and developing our own devices and system solutions in order to offer a comprehensive TSN product portfolio for industrial automation. We will thus enable the consistent networking of IT and OT, as well as different sectors in the sense of the All Electric Society.
Other new communication technologies Consistent communication through to the field
New communication standards such as OPC UA, TSN, SPE, and 5G are currently being created by various committees and in standardization projects. However, these new technologies should not be considered independent of each other – rather, they will form the communication of the future together.
As a technology leader with more than 30 years of experience in industrial communication technology, Phoenix Contact is actively involved in all of the key standardization committees. In these committees, we are helping to shape the new, cross-manufacturer communication standard for automation.
Find out more about the new standards on our webpages.