EMC filter (mains filter) for single-phase AC and DC systems (nominal voltage: up to 230 V AC, up to 220 V DC), for mounting on NS 35, nominal current: 10 A


EMC filters limit high-frequency interference voltages and currents generated by equipment during normal operation and occurring under fault conditions. Using our EMC filters, you ensure smooth operation in environments subject to interference.

EMC filter (mains filter) for single-phase AC and DC systems (nominal voltage: up to 230 V AC, up to 220 V DC), for mounting on NS 35, nominal current: 10 A

EMC filter (mains filter) for single-phase AC and DC systems (nominal voltage: up to 230 V AC, up to 220 V DC), for mounting on NS 35, nominal current: 10 A

EMC filter (mains filter) for single-phase AC and DC systems (nominal voltage: up to 230 V AC, up to 220 V DC), for mounting on NS 35, nominal current: 20 A

EMC filter (mains filter) for single-phase AC and DC systems (nominal voltage: up to 230 V AC, up to 220 V DC), for mounting on NS 35, nominal current: 6 A

EMC filter (mains filter) for single-phase AC and DC systems (nominal voltage: up to 230 V AC, up to 220 V DC), for mounting on NS 35, nominal current: 3 A

EMC filter (mains filter) for single-phase AC and DC systems (nominal voltage: up to 230 V AC, up to 220 V DC), for mounting on NS 35, nominal current: 6 A

EMC filter (mains filter) for single-phase AC and DC systems (nominal voltage: up to 230 V AC, up to 220 V DC), for mounting on NS 35, nominal current: 20 A

Surge protection with filter function for a 2-wire floating signal circuit, e.g., 0(4) ... 20 mA current loop, HART-compatible.

EMC filter (mains filter) for single-phase AC systems, for mounting on NS 35, integrated surge protective device (type 2 SPD), nominal voltage: 230 V AC, nominal current: 10 A

EMC filter (mains filter) for single-phase AC and DC systems (nominal voltage: up to 230 V AC, up to 220 V DC), for mounting on NS 35, nominal current: 1 A
Frequency converters, switching power supplies, and lighting system drivers are often sources of interference in power grids. Some of the EMC interference is mitigated directly at the sources of interference by special filter circuits. However, the remaining interference can propagate and amplify via the supply and control lines. This can have unpredictable effects on controllers, power supplies, sensors, and actuators. Our filters limit the interference directly in front of the potentially susceptible equipment or the sensitive end devices.
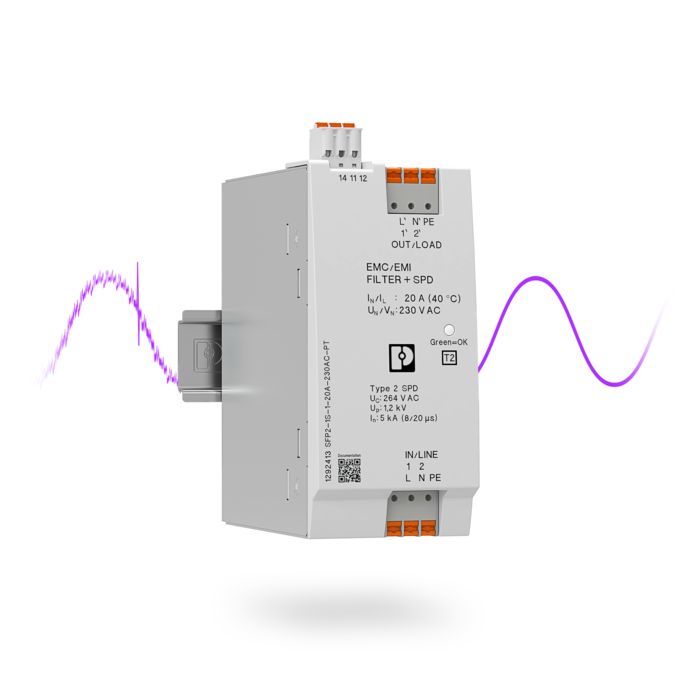
EMC filter with integrated type 2 surge protection
Conventional filters only protect against high-frequency interferences, but not against overvoltage pulses. For effective protection, additional surge protection components are needed. SFP2 filters provide effective protection against surges and high-frequency interference as they feature a surge protection circuit that protects both the input and output side of the filter.

Snap on, connect, ready – with Push-in or screw connection as an option
Thanks to the simple DIN rail mounting and the variable connection technology, using the filters in the control cabinet is child's play. Choose between the fast Push-in connection technology or proven screw connections for connecting the interference suppression filters.
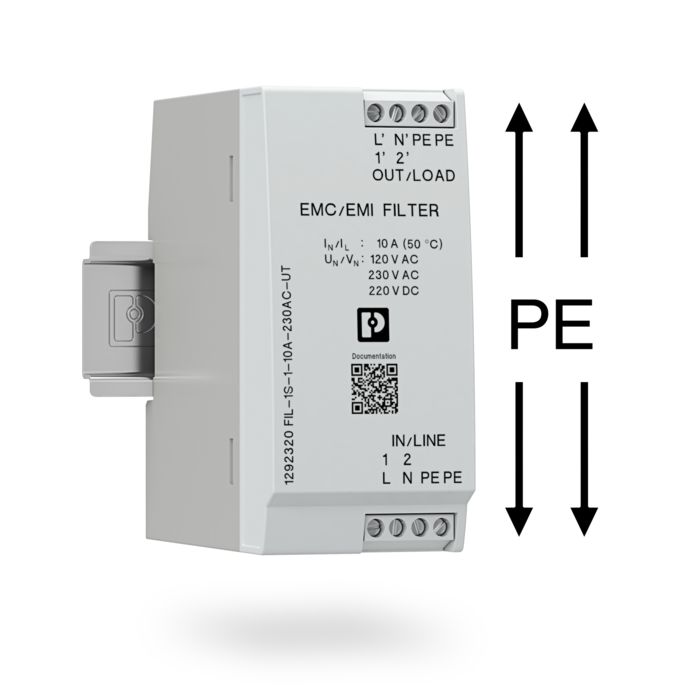

Additional PE terminal points improve the filtering effect of the filters in the plastic housing
The connection of the interference suppression filters to the local protective bonding is realized by additional PE terminal points. This improves the filter effect for high-frequency interferences between the active conductors and the ground potential. This way, an EMC-optimized installation and an improved protective effect is also achieved for EMC filters in plastic housings.