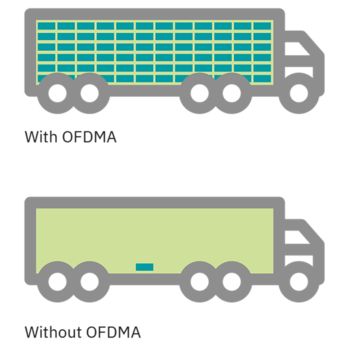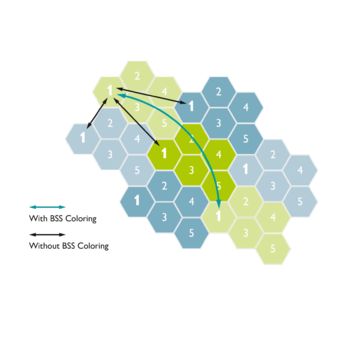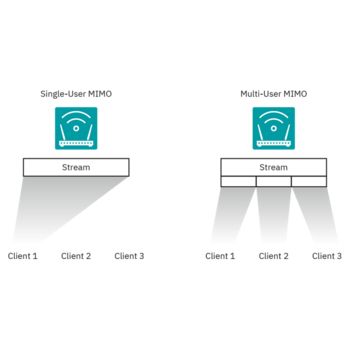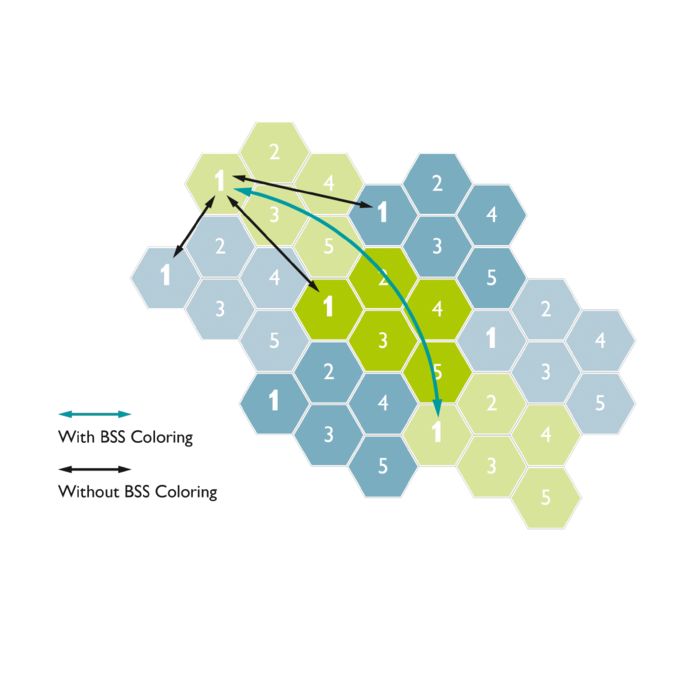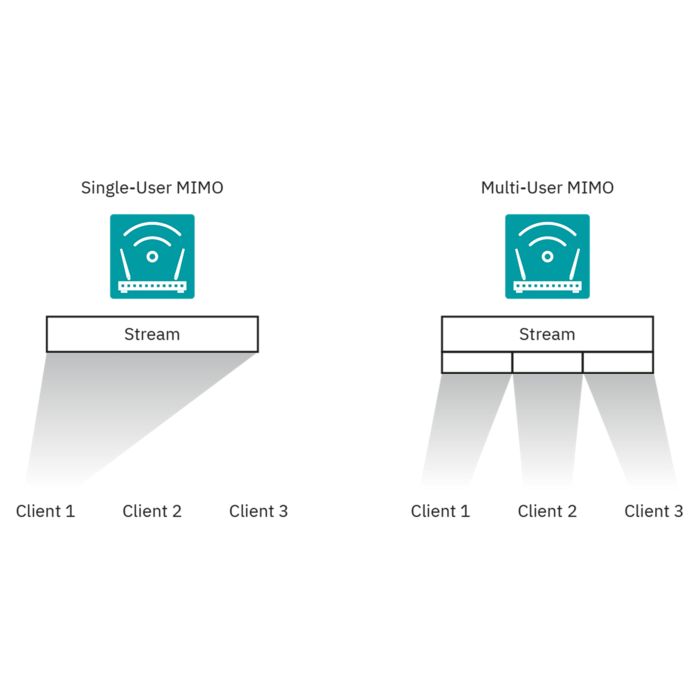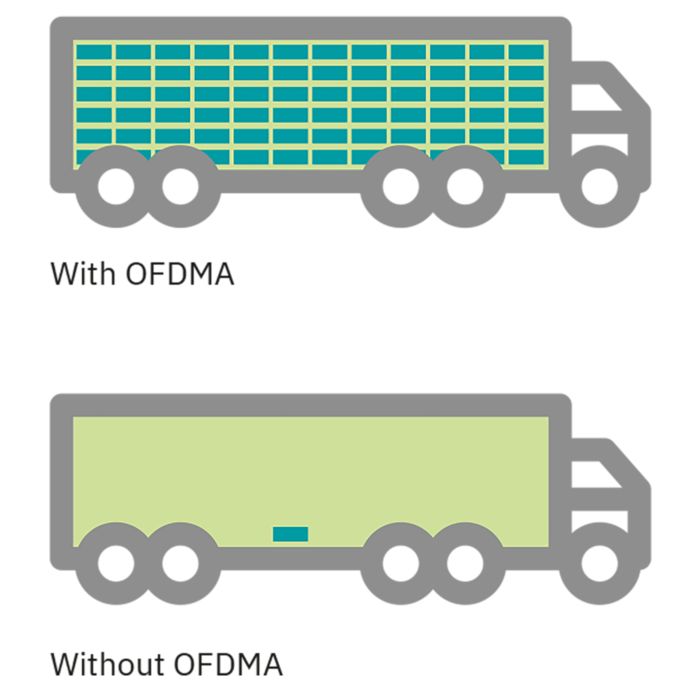
OFDMA (orthogonal frequency-division multiple access) allows the access point to effectively divide channels so that it can communicate with multiple devices (clients) simultaneously on one channel. This technology enables more users to be operated in less time. This significantly improves efficiency and reduces the latency in congested networks considerably. The improvement of the overall QoS thus enables the effective use of the bandwidth in an environment with a high WLAN density.