Industrial 5G In the future, Industrial 5G will enable reliable, wireless networking with high data speeds, high numbers of participants, and extremely low latency times. 5G, the 5th generation of wireless broadband technology, enables users to establish reliable connectivity, which in turn enables flexible, autonomous, and efficient processes from production to logistics.

What exactly is Industrial 5G?
5G is a new cellular standard that, depending on requirements, promises enormous bandwidth in the gigabit range, real-time capability, and high numbers of participants, while offering high-level reliability and security at the same time.
In contrast to previous cellular generations such as 3G and 4G, 5G for the first time also satisfies the industrial sector’s demands, meaning that intelligent wireless communication between machines and applications can be guaranteed. With Industrial 5G, private networks that satisfy all of the prerequisites for flexible, sustainable network connections in mobile or highly flexible applications can also be established, for example.
Industrial 5G is ideal in particular for the field of Industry 4.0. With its high level of flexibility, versatility, usability, and efficiency, 5G will make Industry 4.0, smart factories, and the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) possible.
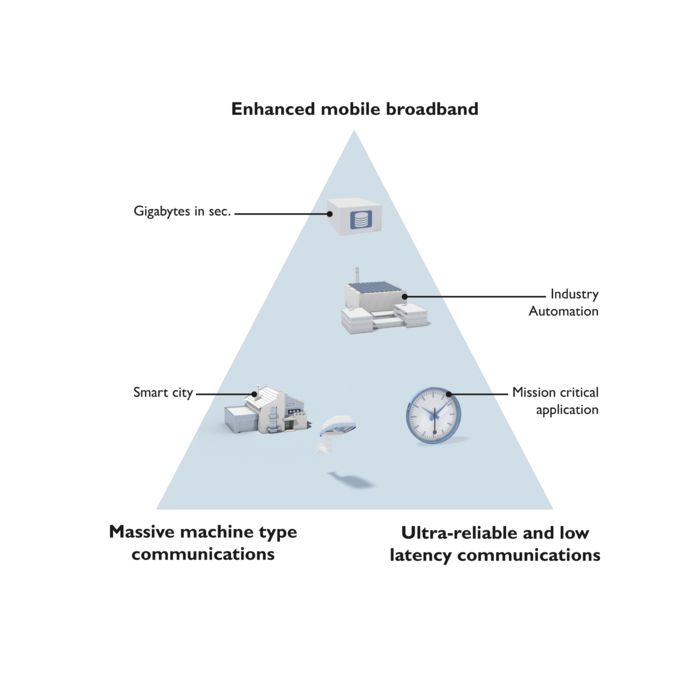
The various characteristics of Industrial 5G can be used depending on application
5G technology’s features and characteristics
Industrial 5G offers users a level of performance that is many times higher when compared to previous cellular standards. Alongside characteristics such as low latency times (ultra-reliable low-latency communication, URLLC), high connection density (massive machine type communication, mMTC), and bandwidth (enhanced mobile broadband, eMBB), the technology features properties such as comprehensive IIoT connectivity and a higher level of flexibility.
Industrial 5G does not, however, provide all of these superlatives at once. Instead, it enables precisely these properties to be assigned to the respective fields of application and individual resources to be attributed in a private 5G network. It thus offers a triangle of functions that can be used depending on the application.
In other words: Today, various wireless technologies (for example, WLAN, WirelessHART, GSM, LTE, etc.) or even wire-based media are used due to differing requirements, but in the future, it will be possible to set up consistent private 5G networks that are adapted to the respective application.
Private networks – an opportunity for the industrial sector
For industry, the ability to build private networks and thus to be able to control the properties and reliability of the 5G network itself is what’s really special about 5G technology. Here, private networks are considered to be distinct from public networks. They are therefore also known as non-public networks (NPNs) or local networks.
In a private 5G network, several antennas are connected to a 5G base station in order to illuminate a factory or private property, for example. This means that the communication infrastructure is completely standalone. The wireless devices in the application will connect to the independent wireless network rather than to the public cellular network.
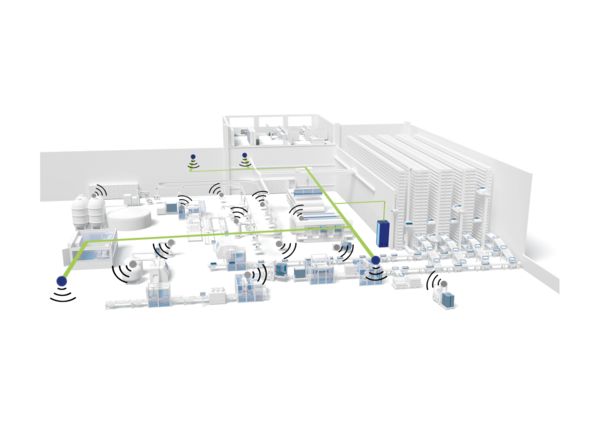
Wireless networking in factory automation
The advantages of a private network are that companies can track, store, analyze, direct, and configure data traffic flexibly to suit their requirements. It therefore offers a key advantage over previous wireless solutions that use license-free frequency bands based on the best-effort principle and have to accept performance losses when the frequency spectrum is heavily occupied.
In addition to this version of a fully isolated, private 5G network, there are hybrid forms in which private and public networks share common resources, such as a base station or the network control tasks. It is also possible to fully integrate private base stations into the public network. To ensure Quality of Service in this case, “virtual private network resources” are realized, for example through network slicing or via APNs.
Industrial 5G areas of application
In principle, there is an infinite number of conceivable applications for Industrial 5G. Due to the high scalability and adaptability of the system, a wide variety of applications with a wide variety of requirements can be integrated:


5G-ACIA represents the interests of the industrial sector in the development of 5G
Our commitment in the area of Industrial 5G
In a collaboration with Quectel and Ericsson, Phoenix Contact has developed the first industrial 5G router for local industrial applications in private 5G networks. Using this 5G router, industrial applications such as machines, controllers, and other devices can be connected to a private 5G network, allowing their coordination in terms of resource utilization, priority, and behavior.
Furthermore, Phoenix Contact is a founding partner, active participant, and member of the board of the 5G-ACIA body (5G Alliance for Connected Industries and Automation). This association of companies strives to represent the interests of industry in the standardization and
regulation of 5G. 5G-ACIA’s aim is to discuss and evaluate the technical, regulatory, and commercial aspects in relation to Industrial 5G.
The progress of 5G in the industrial sector
Although 5G has been discussed for years and the frequencies in most countries have been increased, the potential of 5G in the industrial sector is far from being fully tapped. This is because 5G is not a technology that has been specified in detail and then launched. Instead, it is being launched in several steps or phases, each of which enables different functions.
The first phase began in late 2018 with Release 15, which enabled a broad bandwidth. In the second phase, which occurred in 2020, Release 16 introduced high connection density. In 2022, the third phase took place with Release 17, which enables low latency periods.
Phoenix Contact is coordinating with 5G infrastructure providers to supply seamless 5G solutions and integrate the latest standards into our devices as quickly as possible. This ensures that you are always up to date.
Other new communication technologies Consistent communication through to the field
New communication standards such as OPC UA, TSN, SPE, and 5G are currently being created by various committees and in standardization projects. However, these new technologies should not be considered independent of each other – rather, they will form the communication of the future together.
As a technology leader with more than 30 years of experience in industrial communication technology, Phoenix Contact is actively involved in all of the key standardization committees. In these committees, we are helping to shape the new, cross-manufacturer communication standard for automation.
Find out more about the new standards on our webpages.








