UV LED printing UV LED printing technology is characterized by versatile, durable, and high-quality marking solutions. Our inkjet printers enable precise print images and durable markings thanks to special colorant concepts and curing the marking using UV light.


UV inkjet printing technology Precision meets efficiency
UV inkjet technology has established itself as a versatile and powerful solution for industrial identification. It enables razor-sharp and consistent print images on a wide range of materials. In the electrical and automation industry, it is used in particular for marking materials made of various plastics and metals. The BLUEMARK E.CARD and BLUEMARK ID COLOR printing systems enable the efficient creation of resilient markers for terminals, wires and cables, equipment, and plants.
Printing process Inkjet printing using UV light to cure the print image
UV inkjet printing technology represents a significant advance in digital printing. In contrast to conventional printing processes, in which colorants dry through evaporation, UV LED printing uses ultraviolet light to cure inks or fluids immediately after they are applied to the material. The immediate curing ensures a particularly resilient and durable print surface.
Both the BLUEMARK E.CARD and the BLUEMARK ID COLOR work with UV inkjet technology. However, the printing processes differ in terms of the printhead technology used and the colorants to be processed.
Printheads
In Drop-on-Demand inkjets, two different printhead technologies can be used:
Bubble jet method: Here, a vapor bubble is generated through electrical heating, with the resulting pressure then pushing the drops out of the nozzle. Ink containing a solvent is required to generate the vapor bubble. Bubble jets are used in inexpensive printers, e.g., for private use.
Piezo jet method: Here, the nozzle channels consist of piezo crystals, which are moved by electrical pulses in waves. This then causes the drops to be fired out. Piezo jets are high-quality, durable printheads that are used in UV printing, for example. The BLUEMARK ID and BLUEMARK ID COLOR printers from our portfolio use the piezo jet method.

(1) Card transport system (2) Marking material (3) Printing unit (4) Ink cartridge (5) Drying module (6) UV module
BLUEMARK E.CARD Printing process with bubble jet printhead
The BLUEMARK E.CARD works with thermal inkjet technology. This is a contact-free printing process based on the targeted heating of ink. It is also known as the bubble jet method. An electrical pulse is sent to a heating element in the printhead, which heats the ink up locally. The temperature generates a vapor bubble, which expands explosively. The resulting overpressure sprays a fine ink droplet through a nozzle onto the substrate. Ink containing a solvent is required to generate the vapor bubble. Phoenix Contact has developed a hybrid ink for this, which is both solvent-based and UV-curable.
The UV inkjet printer processes card materials with the help of an automated card transport system. After inserting a stack of material, the cards are automatically fed into the printing process. The printing unit consists of an ink cartridge, a drying module, and a UV module. The printhead is built into the ink cartridge. As the printhead is regularly replaced along with the cartridge, the printer provides a consistently high print quality and requires little maintenance. The printing process is split into two steps.

(1) Transport system (2) Marking material (3) Printing unit (4) Ink cartridge with printhead (5) Drying module (6) UV module (7) Ink drops (8) Vaporizing solvent (9) UV radiation (10) Polymerized fluid
Step 1:
The marking material is transported into the printer using the automated transport system. Once there, the printing unit moves forward over the material and the ink drops are applied via the printhead in the ink cartridge. The solvent is then completely removed from the ink using the drying module, resulting in a solvent-free liquid.
Step 2:
In the second step, the printing unit moves backwards over the marking material. The remaining UV-reactive components of the fluid are polymerized by UV light and permanently cured. The intensive curing of the fluid with UV light makes the marking materials particularly resilient.

(1) Transport system (2) Marking material (3) Printhead (4) UV module (5) Fluid drops (6) UV radiation (7) Polymerized fluid
BLUEMARK ID COLOR Printing process with piezo jet printhead
The BLUEMARK ID COLOR works with piezo jet printing technology. This is also a contact-free printing process. However, this process is not based on heating ink, but on piezo crystals in the nozzle channels of the printhead, which are moved by electrical pulses in waves. The pressure generated by the mechanical movement forces the fluid out of the printhead nozzle and propels individual drops of fluid in the direction of the marking material. The fluid is applied in lines below the printhead through the movement of the material. In the same step, high-intensity UV radiation cures the fluid. The material is not heated by the use of UV LED light, so even plastics that tend to deform when heated can be processed without any problems.
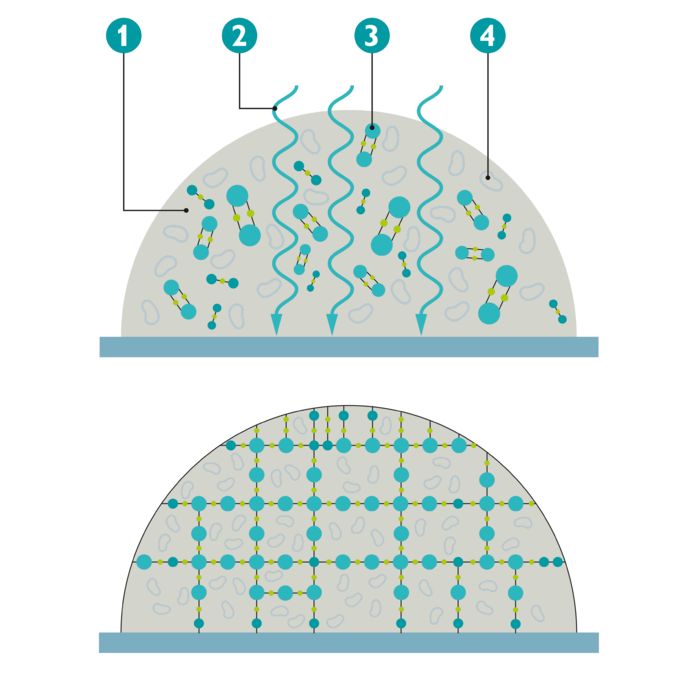
(1) Printing fluid (2) UV radiation (3) Polymers (4) Color pigments
Colorants
Depending on its application, creating identifications with a solvent-based ink requires that the marking cannot be dissolved by other solvents. This method is therefore not suitable for every application. To cure the ink, the component is heated for several minutes following the printing process. Depending on the material and ink used, it is heated to temperatures between +70°C and +200°C. Not all materials are suitable for this process; plastics in particular can warp at high temperatures.
The UV LED printers from Phoenix Contact use solvent-free printing fluid. This fluid consists of three main components: UV initiators, binder material, and color pigments. The key to UV LED printing technology is photochemically induced polymerization. UV radiation converts the fluid initiators into radicals. Radicals are molecules with one free electron. The radicals activate molecules in the bonding components, called monomers, and bond with them to form chains and matrices. Such chains are referred to as polymers. They surround the color pigments and thereby cure the fluid without generating heat.
Light sources

The light spectrum
UV lamps in the form of burners are often used as UV light sources. Their use is associated with high heat generation due to their construction. Burners are particularly powerful, but also have a large variance of emitted UV light. As such, a UV C burner (100 to 280 nm wavelength) also emits light in the UV A (315 to 380 nm) and UV B range (280 to 315 nm).

Wavelength range of UV LEDs
LEDs are used in Phoenix Contact devices. UV LEDs emit light in a very narrow range (UV A) and therefore have significantly lower variance than burners. The UV-induced, photochemical polymerization is often in a wavelength range of 200 to 400 nm. The minimal heat generation is an additional advantage. This allows the creation of smaller and lighter printers, such as the BLUEMARK ID COLOR and the BLUEMARK E.CARD, as well as the processing of heat-sensitive materials such as plastic.
Comparison of inkjet printers Powerful printing systems for versatile identification solutions
 |
 |
|
|---|---|---|
|
BLUEMARK E.CARD
Low-maintenance card printer for efficient marking processes |
BLUEMARK ID COLOR
Versatile card printer for monochrome and CMYK multicolor printing |
|
| Printing process | Thermal inkjet printing with UV LED curing | Piezo inkjet printing with UV LED curing |
| Print resolution | HD printing (600 dpi) | Standard (300 dpi) and HD printing (600 dpi) |
| Printhead | Drop-on-demand inkjet, bubble jet method, printhead built into the ink cartridge | Drop-on-demand inkjet, piezo jet method, printhead is built into the device |
| Cartridge system | Ink and cleaning cartridge | Fluid and cleaning cartridge |
| Color print | ||
| Marking material | UC, UCT, UM sheets and metal labels | UC, UCT, US, UM sheets and metal labels |
| Material feed | Automated material processing of all marking materials without interrupting the print job | Automated material processing of UC, UCT, UM, and metal materials; manual feeding of US materials |
| Magazine extension | Extendable input and output magazine | Extendable input magazine |
| Interfaces | USB, Ethernet, WLAN (additional hardware required) | USB, Ethernet |
| Operation / status display | Touch display or web interface | Touch display |
| Control | Desktop software | Desktop software or touch display |
| Dimensions [width x depth x height] | 570 × 440 × 253 mm | 523 × 675 × 340 mm |
| Weight | < 11 kg | 21 kg |
| View product | View product |